Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/3-21G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2599.032959 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -2599.036707 |
| HF Energy | -2599.032959 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 79.925676 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3324 |
3000 |
8.13 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1514 |
1366 |
38.91 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
721 |
650 |
17.95 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
212 |
191 |
77.23 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A" |
3482 |
3142 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
1003 |
905 |
1.76 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5127.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9026) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4628.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/3-21G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.004 |
1.505 |
0.000 |
| Br2 |
-0.004 |
-0.372 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
0.086 |
2.000 |
0.942 |
| H4 |
0.086 |
2.000 |
-0.942 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| C1 | | 1.8772 | 1.0683 | 1.0683 |
Br2 | 1.8772 | | 2.5543 | 2.5543 | H3 | 1.0683 | 2.5543 | | 1.8846 | H4 | 1.0683 | 2.5543 | 1.8846 | |
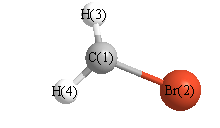 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br2 |
C1 |
H3 |
117.617 |
|
Br2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.617 |
| H3 |
C1 |
H4 |
123.787 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/3-21G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.422 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
-0.067 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.245 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.245 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.168 |
1.342 |
0.000 |
1.353 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.211 |
0.358 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.358 |
-20.973 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.288 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.581 |
0.358 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.358 |
4.277 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.696 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.392 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.239 |
|---|
| xy | 0.358 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.908 |
0.057 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.057 |
4.818 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.752 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
43.112 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.566 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/3-21G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2599.032949 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -2599.032949 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 79.946253 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3327 |
3003 |
7.52 |
103.36 |
0.12 |
0.21 |
| 2 |
A1 |
1512 |
1364 |
40.16 |
2.18 |
0.68 |
0.81 |
| 3 |
A1 |
721 |
651 |
17.28 |
12.36 |
0.28 |
0.44 |
| 4 |
B1 |
150i |
136i |
83.32 |
1.80 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B2 |
3486 |
3147 |
0.00 |
55.48 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
999 |
902 |
1.83 |
4.62 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4947.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9026) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4465.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/3-21G*
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.504 |
| Br2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.372 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.944 |
-2.003 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
-0.944 |
-2.003 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| C1 | | 1.8762 | 1.0679 | 1.0679 |
Br2 | 1.8762 | | 2.5563 | 2.5563 | H3 | 1.0679 | 2.5563 | | 1.8879 | H4 | 1.0679 | 2.5563 | 1.8879 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br2 |
C1 |
H3 |
117.884 |
|
Br2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.884 |
| H3 |
C1 |
H4 |
124.232 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/3-21G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.425 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
-0.066 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.246 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.246 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.344 |
1.344 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.232 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-24.268 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-20.939 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.629 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.683 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.311 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.623 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.964 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.899 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.749 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.812 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
43.104 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.565 |
