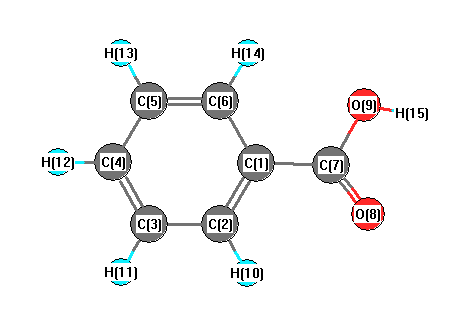
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
4003 |
3614 |
134.72 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3418 |
3086 |
2.90 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3406 |
3075 |
6.47 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3389 |
3060 |
20.33 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3377 |
3049 |
16.61 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3361 |
3035 |
1.20 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1895 |
1711 |
435.65 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1810 |
1634 |
22.44 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1781 |
1608 |
16.09 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1678 |
1515 |
7.60 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1629 |
1470 |
26.64 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1511 |
1364 |
165.45 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1498 |
1352 |
10.54 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1391 |
1256 |
6.72 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1328 |
1199 |
9.06 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1301 |
1175 |
175.42 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1289 |
1163 |
21.81 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1217 |
1099 |
72.95 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1189 |
1073 |
115.88 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
1143 |
1032 |
12.35 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
1111 |
1003 |
2.24 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
843 |
761 |
6.41 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
700 |
632 |
2.54 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A' |
692 |
625 |
66.81 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A' |
543 |
490 |
6.53 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A' |
416 |
375 |
10.65 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A' |
235 |
212 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1198 |
1082 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1172 |
1058 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1126 |
1017 |
3.27 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
999 |
902 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
921 |
832 |
3.01 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
809 |
730 |
220.97 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
782 |
706 |
6.39 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
640 |
578 |
154.25 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
488 |
441 |
15.34 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
469 |
423 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
180 |
163 |
0.56 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
79 |
71 |
1.37 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27507.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9029) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24836.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.170 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.143 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.221 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.168 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.223 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.130 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
0.770 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
O |
-0.561 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
O |
-0.747 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.259 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.212 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.212 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.210 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.258 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.444 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.291 |
-2.079 |
0.000 |
2.447 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-49.234 |
-7.294 |
0.000 |
| y |
-7.294 |
-46.800 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-54.874 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.603 |
-7.294 |
0.000 |
| y |
-7.294 |
5.254 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-6.857 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -13.714 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.434 |
|---|
| xy | -7.294 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
11.686 |
-0.011 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.011 |
14.095 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.465 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
0.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
0.000 |