Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at QCISD(T)/TZVP
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -217.920352 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -217.928186 |
| HF Energy | -217.195979 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 127.788875 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at QCISD(T)/TZVP
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3128 |
3013 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3063 |
2950 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3055 |
2943 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3042 |
2930 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1540 |
1483 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1522 |
1466 |
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1506 |
1451 |
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1462 |
1408 |
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1437 |
1384 |
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1354 |
1304 |
|
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1153 |
1110 |
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1075 |
1036 |
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1041 |
1002 |
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
909 |
876 |
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
452 |
435 |
|
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
269 |
259 |
|
|
|
|
| 17 |
A" |
3127 |
3012 |
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
A" |
3108 |
2993 |
|
|
|
|
| 19 |
A" |
3093 |
2979 |
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
1514 |
1459 |
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
1328 |
1279 |
|
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
1288 |
1241 |
|
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
1215 |
1170 |
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
909 |
875 |
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
776 |
747 |
|
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
227 |
218 |
|
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
122 |
117 |
|
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21355.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9632) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20569.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at QCISD(T)/TZVP
Point Group is Cs
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at QCISD(T)/TZVP
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -217.920776 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -217.196049 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 130.154744 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at QCISD(T)/TZVP
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3137 |
3022 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3122 |
3007 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3114 |
2999 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3090 |
2977 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3057 |
2945 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3046 |
2934 |
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3045 |
2933 |
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1533 |
1476 |
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1520 |
1465 |
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1508 |
1453 |
|
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1487 |
1432 |
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1455 |
1401 |
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1435 |
1382 |
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1398 |
1347 |
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1312 |
1263 |
|
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1293 |
1245 |
|
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1197 |
1153 |
|
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1137 |
1095 |
|
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1097 |
1057 |
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
985 |
948 |
|
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
931 |
896 |
|
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
882 |
850 |
|
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
775 |
747 |
|
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
484 |
466 |
|
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
318 |
307 |
|
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
225 |
217 |
|
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
140 |
135 |
|
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21360.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9632) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20574.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at QCISD(T)/TZVP
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.797 |
0.517 |
0.296 |
| C2 |
-0.597 |
0.659 |
-0.284 |
| C3 |
-1.526 |
-0.488 |
0.118 |
| F4 |
1.395 |
-0.659 |
-0.170 |
| H5 |
1.442 |
1.349 |
-0.000 |
| H6 |
0.766 |
0.454 |
1.389 |
| H7 |
-0.518 |
0.719 |
-1.375 |
| H8 |
-1.000 |
1.617 |
0.067 |
| H9 |
-2.526 |
-0.345 |
-0.300 |
| H10 |
-1.138 |
-1.443 |
-0.241 |
| H11 |
-1.620 |
-0.546 |
1.208 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
F4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 1.5167 | 2.5374 | 1.4004 | 1.0937 | 1.0952 | 2.1359 | 2.1189 | 3.4840 | 2.8065 | 2.7929 |
C2 | 1.5167 | | 1.5297 | 2.3919 | 2.1715 | 2.1684 | 1.0951 | 1.0968 | 2.1741 | 2.1710 | 2.1733 | C3 | 2.5374 | 1.5297 | | 2.9408 | 3.4926 | 2.7852 | 2.1688 | 2.1699 | 1.0931 | 1.0923 | 1.0950 | F4 | 1.4004 | 2.3919 | 2.9408 | | 2.0164 | 2.0167 | 2.6482 | 3.3129 | 3.9359 | 2.6526 | 3.3169 | H5 | 1.0937 | 2.1715 | 3.4926 | 2.0164 | | 1.7859 | 2.4752 | 2.4575 | 4.3246 | 3.8094 | 3.7979 | H6 | 1.0952 | 2.1684 | 2.7852 | 2.0167 | 1.7859 | | 3.0594 | 2.4942 | 3.7854 | 3.1438 | 2.5932 | H7 | 2.1359 | 1.0951 | 2.1688 | 2.6482 | 2.4752 | 3.0594 | | 1.7652 | 2.5137 | 2.5192 | 3.0797 | H8 | 2.1189 | 1.0968 | 2.1699 | 3.3129 | 2.4575 | 2.4942 | 1.7652 | | 2.5119 | 3.0785 | 2.5225 | H9 | 3.4840 | 2.1741 | 1.0931 | 3.9359 | 4.3246 | 3.7854 | 2.5137 | 2.5119 | | 1.7710 | 1.7709 | H10 | 2.8065 | 2.1710 | 1.0923 | 2.6526 | 3.8094 | 3.1438 | 2.5192 | 3.0785 | 1.7710 | | 1.7712 | H11 | 2.7929 | 2.1733 | 1.0950 | 3.3169 | 3.7979 | 2.5932 | 3.0797 | 2.5225 | 1.7709 | 1.7712 | |
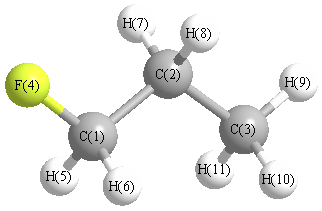 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
112.800 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
108.654 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
107.246 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F4 |
110.099 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
111.554 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.214 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.879 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
110.677 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
110.701 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
110.338 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.322 |
|
F4 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.255 |
| F4 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.191 |
|
H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.353 |
| H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
107.281 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
108.272 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
108.060 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
108.149 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
