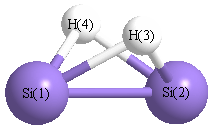Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.019823 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.821510 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 66.617737 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2351 |
2220 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σg |
741 |
700 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σu |
2347 |
2216 |
4.74 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
631i |
595i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
631i |
595i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
373 |
353 |
3.53 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
373 |
353 |
3.53 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2462.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9443) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2325.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.994 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.994 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.466 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.466 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9884 | 1.4719 | 3.4603 |
Si2 | 1.9884 | | 3.4603 | 1.4719 | H3 | 1.4719 | 3.4603 | | 4.9322 | H4 | 3.4603 | 1.4719 | 4.9322 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.055697 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.848957 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.608467 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2213 |
2090 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
627 |
592 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
576 |
544 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Au |
363 |
342 |
26.36 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Bu |
2218 |
2094 |
167.25 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Bu |
316 |
298 |
29.90 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3156.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9443) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2980.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
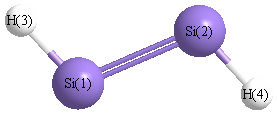
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.059 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.059 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.242 |
1.897 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.242 |
-1.897 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1174 | 1.4986 | 3.2061 |
Si2 | 2.1174 | | 3.2061 | 1.4986 | H3 | 1.4986 | 3.2061 | | 4.5350 | H4 | 3.2061 | 1.4986 | 4.5350 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
124.012 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
124.012 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.077403 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.885168 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.948349 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1677 |
1584 |
10.75 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
985 |
930 |
56.05 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
547 |
517 |
1.54 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A2 |
1109 |
1047 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B1 |
1585 |
1497 |
36.85 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
1210 |
1142 |
423.60 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3556.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9443) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3358.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.103 |
-0.052 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.103 |
-0.052 |
| H3 |
0.996 |
0.000 |
0.725 |
| H4 |
-0.996 |
0.000 |
0.725 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.2062 | 1.6771 | 1.6771 |
Si2 | 2.2062 | | 1.6771 | 1.6771 | H3 | 1.6771 | 1.6771 | | 1.9926 | H4 | 1.6771 | 1.6771 | 1.9926 | |
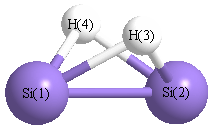 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
48.874 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.874 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.062899 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.864488 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.886889 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2213 |
2090 |
101.86 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1686 |
1592 |
105.32 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1085 |
1025 |
166.69 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
616 |
581 |
16.45 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
448 |
423 |
7.84 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
19 |
18 |
42.18 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3033.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9443) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2864.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.061 |
-1.146 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.061 |
0.977 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.251 |
-0.006 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.470 |
2.376 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1225 | 1.7386 | 3.5614 |
Si2 | 2.1225 | | 1.6399 | 1.4967 | H3 | 1.7386 | 1.6399 | | 2.5065 | H4 | 3.5614 | 1.4967 | 2.5065 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
159.190 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
49.035 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability