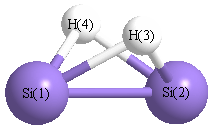Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.142789 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.881836 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 66.927210 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2361 |
2222 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σg |
757 |
712 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σu |
2357 |
2219 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
617i |
581i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
617i |
581i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
429 |
403 |
4.32 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
429 |
403 |
4.32 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2548.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9412) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2399.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.990 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.990 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.452 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.452 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9803 | 1.4614 | 3.4417 |
Si2 | 1.9803 | | 3.4417 | 1.4614 | H3 | 1.4614 | 3.4417 | | 4.9030 | H4 | 3.4417 | 1.4614 | 4.9030 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.175216 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.907633 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.845990 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2211 |
2081 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
620 |
584 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
566 |
533 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Au |
278 |
262 |
38.27 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Bu |
2215 |
2085 |
124.78 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Bu |
273 |
257 |
37.99 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3081.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9412) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2900.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
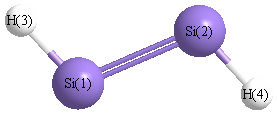
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.055 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.055 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.212 |
1.920 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.212 |
-1.920 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1095 | 1.4893 | 3.2121 |
Si2 | 2.1095 | | 3.2121 | 1.4893 | H3 | 1.4893 | 3.2121 | | 4.5410 | H4 | 3.2121 | 1.4893 | 4.5410 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
125.511 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
125.511 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.207934 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.950290 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.808150 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1643 |
1546 |
2.89 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
936 |
881 |
32.07 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
541 |
509 |
0.69 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A2 |
1120 |
1054 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B1 |
1564 |
1472 |
13.12 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
1214 |
1143 |
412.04 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3509.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9412) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3302.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.107 |
-0.052 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.107 |
-0.052 |
| H3 |
0.990 |
0.000 |
0.723 |
| H4 |
-0.990 |
0.000 |
0.723 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.2139 | 1.6750 | 1.6750 |
Si2 | 2.2139 | | 1.6750 | 1.6750 | H3 | 1.6750 | 1.6750 | | 1.9806 | H4 | 1.6750 | 1.6750 | 1.9806 | |
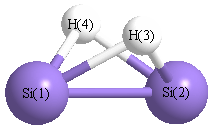 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
48.635 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.635 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.189833 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.928082 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.046194 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2218 |
2088 |
82.17 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1670 |
1572 |
58.73 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1127 |
1061 |
136.75 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
625 |
588 |
17.22 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
460 |
433 |
5.11 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
132 |
124 |
37.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3116.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9412) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2933.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.060 |
-1.144 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.060 |
0.976 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.241 |
-0.017 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.448 |
2.373 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1195 | 1.7209 | 3.5532 |
Si2 | 2.1195 | | 1.6365 | 1.4868 | H3 | 1.7209 | 1.6365 | | 2.5180 | H4 | 3.5532 | 1.4868 | 2.5180 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
160.002 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
49.109 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability