Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -244.821972 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -243.928102 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 123.497522 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3804 |
3689 |
|
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3779 |
3665 |
|
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3639 |
3530 |
|
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1827 |
1772 |
|
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1623 |
1574 |
|
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1437 |
1394 |
|
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1239 |
1202 |
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1080 |
1048 |
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
959 |
930 |
|
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
586 |
568 |
|
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
487 |
472 |
|
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
784 |
760 |
|
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
591 |
573 |
|
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
481 |
467 |
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
258i |
251i |
|
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11028.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9699) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10696.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.130 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-0.065 |
1.341 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.140 |
-0.605 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
-1.091 |
-0.683 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.018 |
-0.122 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.106 |
-1.607 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.851 |
-0.086 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.2128 | 1.3565 | 1.3610 | 2.0334 | 2.0595 | 1.8635 |
O2 | 1.2128 | | 2.2891 | 2.2695 | 2.5452 | 3.1724 | 2.2861 | N3 | 1.3565 | 2.2891 | | 2.2326 | 1.0022 | 1.0026 | 3.0354 | O4 | 1.3610 | 2.2695 | 2.2326 | | 3.1594 | 2.3837 | 0.9660 | H5 | 2.0334 | 2.5452 | 1.0022 | 3.1594 | | 1.7430 | 3.8688 | H6 | 2.0595 | 3.1724 | 1.0026 | 2.3837 | 1.7430 | | 3.3251 | H7 | 1.8635 | 2.2861 | 3.0354 | 0.9660 | 3.8688 | 3.3251 | |
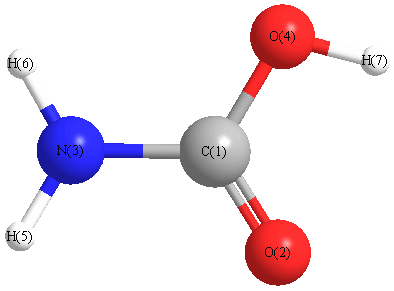 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
H5 |
118.332 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
120.886 |
| C1 |
O4 |
H7 |
105.142 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
125.902 |
| O2 |
C1 |
O4 |
123.614 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
O4 |
110.484 |
| H5 |
N3 |
H6 |
120.782 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -244.785205 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -243.927685 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 123.409588 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
