Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at BLYP/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -117.190063 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -117.194225 |
| HF Energy | -117.190063 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.376946 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3176 |
3151 |
27.57 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
3089 |
3064 |
7.05 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
3060 |
3035 |
18.75 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
1505 |
1493 |
1.30 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A1 |
1249 |
1239 |
0.84 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A1 |
1019 |
1011 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A1 |
415 |
412 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A2 |
746 |
740 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A2 |
535 |
531 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
B1 |
989 |
981 |
13.07 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
B1 |
769 |
763 |
65.44 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B1 |
521 |
517 |
11.58 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
B2 |
3174 |
3148 |
8.12 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
B2 |
3083 |
3058 |
10.43 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B2 |
1502 |
1490 |
0.40 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B2 |
1407 |
1395 |
2.89 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B2 |
1211 |
1201 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B2 |
920 |
913 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14185.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9919) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14070.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at BLYP/6-31G*
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.446 |
| H2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.543 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
1.239 |
-0.197 |
| C4 |
0.000 |
-1.239 |
-0.197 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
2.176 |
0.365 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-2.176 |
0.365 |
| H7 |
0.000 |
1.310 |
-1.289 |
| H8 |
0.000 |
-1.310 |
-1.289 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
H2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.0974 | 1.3964 | 1.3964 | 2.1775 | 2.1775 | 2.1738 | 2.1738 |
H2 | 1.0974 | | 2.1369 | 2.1369 | 2.4746 | 2.4746 | 3.1205 | 3.1205 | C3 | 1.3964 | 2.1369 | | 2.4789 | 1.0924 | 3.4615 | 1.0939 | 2.7731 | C4 | 1.3964 | 2.1369 | 2.4789 | | 3.4615 | 1.0924 | 2.7731 | 1.0939 | H5 | 2.1775 | 2.4746 | 1.0924 | 3.4615 | | 4.3521 | 1.8670 | 3.8583 | H6 | 2.1775 | 2.4746 | 3.4615 | 1.0924 | 4.3521 | | 3.8583 | 1.8670 | H7 | 2.1738 | 3.1205 | 1.0939 | 2.7731 | 1.8670 | 3.8583 | | 2.6196 | H8 | 2.1738 | 3.1205 | 2.7731 | 1.0939 | 3.8583 | 1.8670 | 2.6196 | |
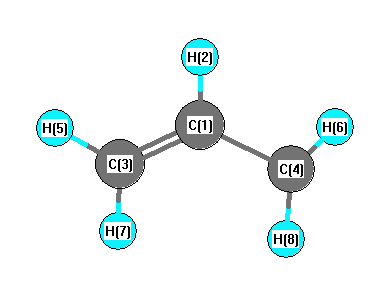 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C3 |
H5 |
121.596 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H7 |
121.114 |
| C1 |
C4 |
H6 |
121.596 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
H8 |
121.114 |
| H2 |
C1 |
C3 |
117.428 |
|
H2 |
C1 |
C4 |
117.428 |
| C3 |
C1 |
C4 |
125.143 |
|
H5 |
C3 |
H7 |
117.290 |
| H6 |
C4 |
H8 |
117.290 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Electronic state
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.003 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.104 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.304 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.304 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.084 |
0.084 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-21.459 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.739 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-17.572 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.803 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.776 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.027 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 4.054 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.720 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.818 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
7.623 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.685 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
50.769 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.125 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at BLYP/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -117.190063 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -117.194226 |
| HF Energy | -117.190063 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.375585 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3176 |
3150 |
26.90 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3173 |
3147 |
8.90 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3089 |
3064 |
6.86 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3082 |
3058 |
10.54 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3060 |
3035 |
18.77 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1505 |
1493 |
1.30 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1502 |
1490 |
0.40 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1407 |
1396 |
2.89 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1249 |
1239 |
0.84 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1211 |
1201 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1020 |
1011 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
920 |
913 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
416 |
412 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
989 |
981 |
13.05 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
769 |
763 |
65.52 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A" |
746 |
740 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A" |
536 |
531 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A" |
522 |
517 |
11.48 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14185.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9919) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14070.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at BLYP/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.463 |
0.000 |
| H2 |
-0.066 |
1.554 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-1.231 |
-0.224 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
1.243 |
-0.178 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-2.188 |
0.291 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
2.185 |
0.374 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.274 |
-1.316 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
1.276 |
-1.267 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
H2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.0930 | 1.4104 | 1.3982 | 2.1944 | 2.1870 | 2.1881 | 2.1503 |
H2 | 1.0930 | | 2.1262 | 2.1711 | 2.4690 | 2.5420 | 3.1135 | 3.1247 | C3 | 1.4104 | 2.1262 | | 2.4743 | 1.0861 | 3.4687 | 1.0920 | 2.7159 | C4 | 1.3982 | 2.1711 | 2.4743 | | 3.4620 | 1.0926 | 2.7619 | 1.0899 | H5 | 2.1944 | 2.4690 | 1.0861 | 3.4620 | | 4.3737 | 1.8477 | 3.7981 | H6 | 2.1870 | 2.5420 | 3.4687 | 1.0926 | 4.3737 | | 3.8502 | 1.8766 | H7 | 2.1881 | 3.1135 | 1.0920 | 2.7619 | 1.8477 | 3.8502 | | 2.5509 | H8 | 2.1503 | 3.1247 | 2.7159 | 1.0899 | 3.7981 | 1.8766 | 2.5509 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C3 |
H5 |
122.512 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H7 |
121.430 |
| C1 |
C4 |
H6 |
122.335 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
H8 |
119.069 |
| H2 |
C1 |
C3 |
115.698 |
|
H2 |
C1 |
C4 |
120.778 |
| C3 |
C1 |
C4 |
123.524 |
|
H5 |
C3 |
H7 |
116.058 |
| H6 |
C4 |
H8 |
118.596 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.003 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.104 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.304 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.304 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.084 |
0.000 |
0.084 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.738 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
-17.572 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-21.459 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.777 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
2.027 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.804 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.607 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.167 |
|---|
| xy | -0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.624 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
4.686 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.818 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
50.773 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.126 |
