Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at BLYP/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -129.256379 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -129.256379 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 32.887921 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/STO-3G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3278 |
3033 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
1715 |
1587 |
4.14 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
1300 |
1203 |
0.58 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
B1 |
580i |
536i |
221.68 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B2 |
3449 |
3191 |
32.55 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
1129 |
1045 |
1.75 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5145.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9252) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4761.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
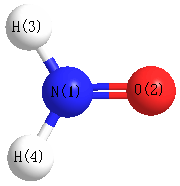
Geometric Data calculated at BLYP/STO-3G
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.575 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.791 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.899 |
-1.152 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
-0.899 |
-1.152 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
O2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.3656 | 1.0678 | 1.0678 |
O2 | 1.3656 | | 2.1403 | 2.1403 | H3 | 1.0678 | 2.1403 | | 1.7972 | H4 | 1.0678 | 2.1403 | 1.7972 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| O2 |
N1 |
H3 |
122.698 |
|
O2 |
N1 |
H4 |
122.698 |
| H3 |
N1 |
H4 |
114.605 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.251 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.106 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.179 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.179 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.052 |
2.052 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-10.878 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-9.137 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.264 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.678 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.934 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.743 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.486 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.741 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.245 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.957 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.702 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
17.680 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.205 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at BLYP/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -129.260080 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -129.262581 |
| HF Energy | -129.260080 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 32.542044 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/STO-3G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3126 |
2892 |
18.71 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1735 |
1605 |
3.84 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1239 |
1146 |
0.45 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
706 |
653 |
141.72 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A" |
3305 |
3058 |
58.80 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
1230 |
1138 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5670.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9252) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5246.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at BLYP/STO-3G
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
-0.054 |
0.600 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-0.054 |
-0.788 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
0.404 |
1.050 |
0.874 |
| H4 |
0.404 |
1.050 |
-0.874 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
O2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.3882 | 1.0841 | 1.0841 |
O2 | 1.3882 | | 2.0862 | 2.0862 | H3 | 1.0841 | 2.0862 | | 1.7473 | H4 | 1.0841 | 2.0862 | 1.7473 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| O2 |
N1 |
H3 |
114.531 |
|
O2 |
N1 |
H4 |
114.531 |
| H3 |
N1 |
H4 |
107.389 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.235 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.099 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.258 |
1.549 |
0.000 |
1.995 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-10.462 |
1.180 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.180 |
-10.113 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.448 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.682 |
1.180 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.180 |
-0.158 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.840 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.679 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.350 |
|---|
| xy | 1.180 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.384 |
0.221 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.221 |
1.660 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.986 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
17.842 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.224 |
