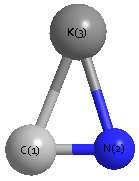Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at BLYP/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.786383 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.785745 |
| HF Energy | -692.786383 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 60.929610 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at BLYP/6-311G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.308 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.278 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.454 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.5863 | 3.7624 |
C2 | 2.5863 | | 1.1761 | N3 | 3.7624 | 1.1761 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.693 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.416 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.277 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.524 |
11.524 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.436 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.436 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.538 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.551 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.551 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-7.102 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -14.203 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.713 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.713 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.368 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
100.595 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.030 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at BLYP/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.788385 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -692.788385 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.312017 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at BLYP/6-311G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.212 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.409 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.224 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.6208 | 2.4360 |
C2 | 3.6208 | | 1.1848 | N3 | 2.4360 | 1.1848 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.699 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.228 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.470 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.604 |
11.604 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.384 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.384 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.013 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.814 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.814 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.629 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -19.258 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.710 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.710 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.540 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
89.821 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.477 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at BLYP/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.792861 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.792720 |
| HF Energy | -692.792861 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 68.401059 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at BLYP/6-311G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.045 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.630 |
-1.631 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.540 |
-1.438 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.7488 | 2.5408 |
C2 | 2.7488 | | 1.1851 | N3 | 2.5408 | 1.1851 | |
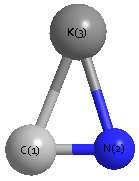 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
67.387 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
87.109 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
25.504 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.635 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.248 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.387 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.469 |
9.738 |
0.000 |
9.749 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.647 |
1.070 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.070 |
-26.465 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.617 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.606 |
1.070 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.070 |
-0.833 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.439 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.878 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.182 |
|---|
| xy | 1.070 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.937 |
-0.264 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.264 |
5.645 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.850 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
71.775 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.472 |