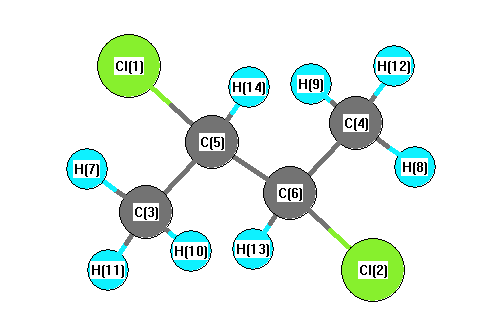
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
3058 |
3063 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
3050 |
3055 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
3008 |
3013 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Ag |
2974 |
2979 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Ag |
1425 |
1428 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Ag |
1421 |
1423 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Ag |
1356 |
1358 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
Ag |
1342 |
1344 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
Ag |
1208 |
1210 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
Ag |
1128 |
1130 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
Ag |
1096 |
1098 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
Ag |
986 |
987 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
Ag |
813 |
814 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Ag |
639 |
640 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
Ag |
461 |
461 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
Ag |
323 |
324 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
Ag |
266 |
266 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
Ag |
229 |
230 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
Au |
3059 |
3064 |
20.31 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
Au |
3051 |
3056 |
31.66 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
Au |
3021 |
3026 |
7.49 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
Au |
2974 |
2978 |
20.98 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
Au |
1425 |
1427 |
10.11 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
Au |
1419 |
1422 |
10.32 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
Au |
1355 |
1357 |
13.91 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
Au |
1275 |
1277 |
6.08 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
Au |
1152 |
1154 |
37.88 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
Au |
1053 |
1055 |
9.38 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
Au |
983 |
985 |
21.17 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
Au |
943 |
944 |
20.68 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
Au |
585 |
586 |
90.27 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
Au |
341 |
342 |
4.15 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
Au |
325 |
326 |
3.50 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
Au |
239 |
239 |
3.02 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
Au |
199 |
199 |
4.33 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
Au |
66 |
66 |
2.79 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24123.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1.0016) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24162.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Cl |
-0.133 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Cl |
-0.133 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.091 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.091 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.073 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.073 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.022 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.022 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.032 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.032 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.020 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.020 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.041 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.041 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-50.415 |
1.912 |
-3.452 |
| y |
1.912 |
-53.072 |
3.265 |
| z |
-3.452 |
3.265 |
-54.533 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.388 |
1.912 |
-3.452 |
| y |
1.912 |
-0.599 |
3.265 |
| z |
-3.452 |
3.265 |
-2.790 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.579 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.658 |
|---|
| xy | 1.912 |
|---|
| xz | -3.452 |
|---|
| yz | 3.265 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.207 |
-0.422 |
0.615 |
| y |
-0.422 |
9.176 |
-2.413 |
| z |
0.615 |
-2.413 |
11.006 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
0.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
0.000 |