Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at BLYP/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -158.373980 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -158.384479 |
| HF Energy | -158.373980 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 129.334276 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
|
Au |
122 |
121 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
210 |
210 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
248 |
247 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
253 |
252 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
413 |
412 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
723 |
721 |
3.45 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
800 |
798 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
814 |
812 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
950 |
948 |
0.96 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
956 |
954 |
5.46 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
985 |
982 |
1.01 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1025 |
1023 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1138 |
1135 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
1183 |
1180 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
1270 |
1267 |
0.17 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1299 |
1296 |
3.28 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
1314 |
1311 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1359 |
1355 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1388 |
1385 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1389 |
1386 |
5.28 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1466 |
1462 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1473 |
1469 |
2.07 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
1481 |
1478 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
1483 |
1479 |
15.93 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1487 |
1484 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1494 |
1491 |
9.30 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
2927 |
2919 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
2935 |
2928 |
52.52 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
2941 |
2933 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
2949 |
2941 |
100.90 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
2949 |
2942 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
2964 |
2956 |
24.60 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
3001 |
2993 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
3006 |
2999 |
157.87 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
3006 |
2999 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
3008 |
3000 |
109.19 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28203.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9975) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28133.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at BLYP/6-311G*
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.423 |
0.646 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.423 |
-0.646 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.423 |
1.935 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-0.423 |
-1.935 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.089 |
0.643 |
0.881 |
| H6 |
-1.089 |
0.643 |
-0.881 |
| H7 |
1.089 |
-0.643 |
0.881 |
| H8 |
1.089 |
-0.643 |
-0.881 |
| H9 |
-0.211 |
2.834 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
1.073 |
1.988 |
0.888 |
| H11 |
1.073 |
1.988 |
-0.888 |
| H12 |
0.211 |
-2.834 |
0.000 |
| H13 |
-1.073 |
-1.988 |
0.888 |
| H14 |
-1.073 |
-1.988 |
-0.888 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
| C1 | | 1.5443 | 1.5420 | 2.5811 | 1.1041 | 1.1041 | 2.1735 | 2.1735 | 2.1985 | 2.1972 | 2.1972 | 3.5376 | 2.8547 | 2.8547 |
C2 | 1.5443 | | 2.5811 | 1.5420 | 2.1735 | 2.1735 | 1.1041 | 1.1041 | 3.5376 | 2.8547 | 2.8547 | 2.1985 | 2.1972 | 2.1972 | C3 | 1.5420 | 2.5811 | | 3.9616 | 2.1749 | 2.1749 | 2.8049 | 2.8049 | 1.1004 | 1.1014 | 1.1014 | 4.7740 | 4.2916 | 4.2916 | C4 | 2.5811 | 1.5420 | 3.9616 | | 2.8049 | 2.8049 | 2.1749 | 2.1749 | 4.7740 | 4.2916 | 4.2916 | 1.1004 | 1.1014 | 1.1014 | H5 | 1.1041 | 2.1735 | 2.1749 | 2.8049 | | 1.7617 | 2.5294 | 3.0824 | 2.5191 | 2.5460 | 3.0999 | 3.8158 | 2.6317 | 3.1706 | H6 | 1.1041 | 2.1735 | 2.1749 | 2.8049 | 1.7617 | | 3.0824 | 2.5294 | 2.5191 | 3.0999 | 2.5460 | 3.8158 | 3.1706 | 2.6317 | H7 | 2.1735 | 1.1041 | 2.8049 | 2.1749 | 2.5294 | 3.0824 | | 1.7617 | 3.8158 | 2.6317 | 3.1706 | 2.5191 | 2.5460 | 3.0999 | H8 | 2.1735 | 1.1041 | 2.8049 | 2.1749 | 3.0824 | 2.5294 | 1.7617 | | 3.8158 | 3.1706 | 2.6317 | 2.5191 | 3.0999 | 2.5460 | H9 | 2.1985 | 3.5376 | 1.1004 | 4.7740 | 2.5191 | 2.5191 | 3.8158 | 3.8158 | | 1.7757 | 1.7757 | 5.6842 | 4.9786 | 4.9786 | H10 | 2.1972 | 2.8547 | 1.1014 | 4.2916 | 2.5460 | 3.0999 | 2.6317 | 3.1706 | 1.7757 | | 1.7752 | 4.9786 | 4.5185 | 4.8547 | H11 | 2.1972 | 2.8547 | 1.1014 | 4.2916 | 3.0999 | 2.5460 | 3.1706 | 2.6317 | 1.7757 | 1.7752 | | 4.9786 | 4.8547 | 4.5185 | H12 | 3.5376 | 2.1985 | 4.7740 | 1.1004 | 3.8158 | 3.8158 | 2.5191 | 2.5191 | 5.6842 | 4.9786 | 4.9786 | | 1.7757 | 1.7757 | H13 | 2.8547 | 2.1972 | 4.2916 | 1.1014 | 2.6317 | 3.1706 | 2.5460 | 3.0999 | 4.9786 | 4.5185 | 4.8547 | 1.7757 | | 1.7752 | H14 | 2.8547 | 2.1972 | 4.2916 | 1.1014 | 3.1706 | 2.6317 | 3.0999 | 2.5460 | 4.9786 | 4.8547 | 4.5185 | 1.7757 | 1.7752 | |
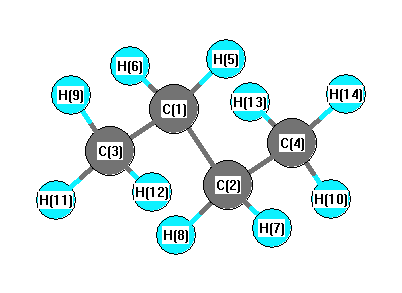 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C4 |
113.500 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.171 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.171 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.515 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.353 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H12 |
30.737 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C3 |
113.500 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.171 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.171 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H10 |
17.151 |
| C2 |
C4 |
H13 |
111.353 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H14 |
111.353 |
| C3 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.441 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.441 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.441 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.441 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
105.832 |
|
H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
105.832 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.503 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H12 |
142.252 |
| H10 |
C4 |
H13 |
94.767 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H14 |
114.612 |
| H11 |
C3 |
H12 |
94.265 |
|
H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.398 |
Electronic energy levels
Electronic state
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at BLYP/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.365 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.365 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.582 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.582 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.195 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.191 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.191 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.195 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.191 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.191 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.365 |
-0.450 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.450 |
-29.806 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.576 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.174 |
-0.450 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.450 |
-0.836 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.010 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.019 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.441 |
|---|
| xy | -0.450 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.998 |
0.240 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.240 |
8.385 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.669 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
121.731 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.033 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at BLYP/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -158.372555 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 130.998770 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at BLYP/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3018 |
3010 |
59.34 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3003 |
2996 |
1.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2959 |
2951 |
19.73 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2952 |
2945 |
53.33 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2928 |
2921 |
14.67 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1495 |
1492 |
1.95 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1487 |
1484 |
5.24 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1467 |
1463 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1393 |
1389 |
3.22 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1342 |
1339 |
1.12 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1289 |
1286 |
0.14 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1167 |
1164 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1050 |
1047 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
970 |
967 |
0.40 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
812 |
810 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
770 |
768 |
1.44 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
315 |
314 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
255 |
254 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
109 |
108 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3011 |
3003 |
68.81 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3005 |
2997 |
118.36 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
2960 |
2953 |
53.60 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
2950 |
2943 |
20.39 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
2930 |
2923 |
32.25 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1490 |
1486 |
11.75 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1481 |
1478 |
9.97 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1465 |
1461 |
0.39 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1387 |
1384 |
6.34 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1348 |
1344 |
3.79 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1267 |
1264 |
0.49 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
1125 |
1123 |
2.24 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
954 |
952 |
2.05 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
933 |
931 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
736 |
734 |
3.89 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
423 |
422 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
208 |
207 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28225.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9975) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28155.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at BLYP/6-311G*
Point Group is C2h
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
