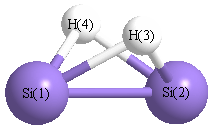Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at CISD/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.001184 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.822502 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 67.131703 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CISD/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2403 |
2225 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σg |
777 |
719 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σu |
2397 |
2220 |
5.48 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
607i |
562i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Πg |
607i |
562i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
425 |
394 |
1.68 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Πu |
425 |
394 |
1.68 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2606.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9258) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2413.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CISD/6-31G*
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.986 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.986 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.451 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.451 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9717 | 1.4656 | 3.4373 |
Si2 | 1.9717 | | 3.4373 | 1.4656 | H3 | 1.4656 | 3.4373 | | 4.9029 | H4 | 3.4373 | 1.4656 | 4.9029 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at CISD/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.034595 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.849348 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.010370 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CISD/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2260 |
2092 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
637 |
590 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
583 |
540 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Au |
541 |
501 |
1.31 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Bu |
2263 |
2095 |
185.98 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Bu |
330 |
306 |
42.48 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3307.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9258) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3061.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
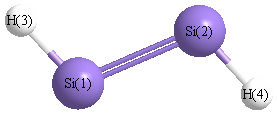
Geometric Data calculated at CISD/6-31G*
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.051 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.051 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.227 |
1.902 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.227 |
-1.902 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1024 | 1.4927 | 3.1976 |
Si2 | 2.1024 | | 3.1976 | 1.4927 | H3 | 1.4927 | 3.1976 | | 4.5261 | H4 | 3.1976 | 1.4927 | 4.5261 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
124.741 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
124.741 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at CISD/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.061275 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.885302 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.165117 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CISD/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1698 |
1572 |
12.70 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
1010 |
935 |
63.95 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
564 |
522 |
1.34 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A2 |
1105 |
1023 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B1 |
1607 |
1488 |
40.37 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
1217 |
1126 |
452.10 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3599.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9258) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3332.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CISD/6-31G*
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.099 |
-0.052 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.099 |
-0.052 |
| H3 |
0.993 |
0.000 |
0.729 |
| H4 |
-0.993 |
0.000 |
0.729 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1974 | 1.6745 | 1.6745 |
Si2 | 2.1974 | | 1.6745 | 1.6745 | H3 | 1.6745 | 1.6745 | | 1.9862 | H4 | 1.6745 | 1.6745 | 1.9862 | |
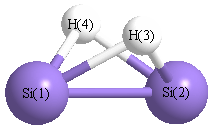 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
48.994 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.994 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at CISD/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.045158 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -578.865033 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.243006 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at CISD/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2268 |
2100 |
102.86 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1719 |
1592 |
118.14 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1083 |
1003 |
174.43 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
635 |
588 |
20.91 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
451 |
418 |
9.37 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
52 |
49 |
47.72 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3104.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9258) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2873.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at CISD/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.060 |
-1.139 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.060 |
0.970 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.254 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.434 |
2.375 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1092 | 1.7394 | 3.5487 |
Si2 | 2.1092 | | 1.6332 | 1.4894 | H3 | 1.7394 | 1.6332 | | 2.5122 | H4 | 3.5487 | 1.4894 | 2.5122 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
160.618 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
49.071 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability