Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3749 |
3587 |
32.45 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3616 |
3459 |
33.25 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3156 |
3019 |
28.40 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3152 |
3016 |
2.93 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3135 |
2999 |
38.61 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3133 |
2997 |
18.32 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3063 |
2930 |
14.91 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3059 |
2927 |
34.45 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3040 |
2908 |
37.66 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1818 |
1740 |
258.73 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1644 |
1573 |
119.79 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1541 |
1474 |
16.07 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1525 |
1459 |
11.15 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1517 |
1451 |
1.81 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1510 |
1445 |
0.68 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1440 |
1377 |
51.08 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1426 |
1364 |
22.68 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1414 |
1353 |
4.95 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1347 |
1289 |
1.51 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1297 |
1241 |
95.02 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1208 |
1156 |
3.48 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1144 |
1094 |
5.80 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1138 |
1088 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1068 |
1022 |
6.71 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
986 |
944 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
940 |
899 |
2.75 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
931 |
890 |
3.69 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
779 |
746 |
7.27 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
764 |
731 |
3.84 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
616 |
589 |
5.81 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
603 |
577 |
15.01 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
476 |
455 |
3.04 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
326 |
312 |
0.96 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
290 |
278 |
4.82 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
244 |
234 |
5.84 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
242 |
232 |
0.44 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
217 |
208 |
1.31 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
127 |
121 |
228.65 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
28 |
27 |
8.49 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28854.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9567) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27605.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
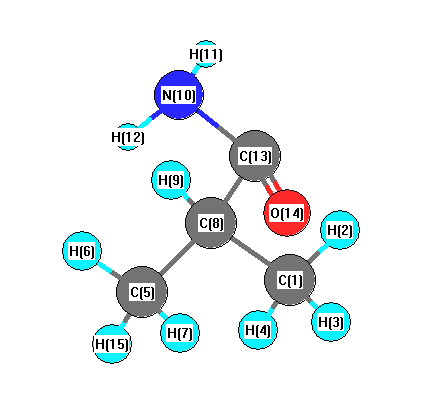
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.507 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.169 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.197 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.507 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.169 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.198 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.216 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
N |
-0.794 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.359 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.353 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.166 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.621 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.520 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.315 |
-0.002 |
-3.552 |
3.566 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
-0.286 |
0.148 |
-3.559 |
3.573 |
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-31.977 |
0.003 |
4.755 |
| y |
0.003 |
-37.663 |
0.001 |
| z |
4.755 |
0.001 |
-38.331 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.020 |
0.003 |
4.755 |
| y |
0.003 |
-2.509 |
0.001 |
| z |
4.755 |
0.001 |
-3.511 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.022 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.686 |
|---|
| xy | 0.003 |
|---|
| xz | 4.755 |
|---|
| yz | 0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
172.424 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.131 |