Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -131.048000 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -131.048000 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 35.259443 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3446 |
3313 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
1676 |
1611 |
11.13 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
1440 |
1385 |
8.38 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
B1 |
304i |
292i |
171.95 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B2 |
3574 |
3436 |
0.87 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
1271 |
1222 |
1.39 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5551.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9614) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5337.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
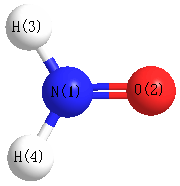
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.535 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.731 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.875 |
-1.051 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
-0.875 |
-1.051 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
O2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.2667 | 1.0152 | 1.0152 |
O2 | 1.2667 | | 1.9851 | 1.9851 | H3 | 1.0152 | 1.9851 | | 1.7496 | H4 | 1.0152 | 1.9851 | 1.7496 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| O2 |
N1 |
H3 |
120.496 |
|
O2 |
N1 |
H4 |
120.496 |
| H3 |
N1 |
H4 |
119.009 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.220 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.341 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.280 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.280 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.953 |
2.953 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-12.117 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-9.729 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-10.545 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.981 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.602 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.379 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.757 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.388 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.151 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.773 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.699 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
16.767 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.095 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -131.048156 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -131.050540 |
| HF Energy | -131.048156 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 35.226585 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3418 |
3287 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1675 |
1610 |
11.29 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1428 |
1373 |
8.12 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
415 |
399 |
167.69 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A" |
3542 |
3406 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
1287 |
1238 |
1.11 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5882.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9614) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5655.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
-0.021 |
0.539 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-0.021 |
-0.730 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
0.160 |
1.036 |
0.869 |
| H4 |
0.160 |
1.036 |
-0.869 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
O2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.2688 | 1.0173 | 1.0173 |
O2 | 1.2688 | | 1.9763 | 1.9763 | H3 | 1.0173 | 1.9763 | | 1.7381 | H4 | 1.0173 | 1.9763 | 1.7381 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| O2 |
N1 |
H3 |
119.238 |
|
O2 |
N1 |
H4 |
119.238 |
| H3 |
N1 |
H4 |
117.358 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.220 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.338 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.279 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.279 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.527 |
2.867 |
0.000 |
2.915 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-12.026 |
0.534 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.534 |
-10.677 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.801 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.787 |
0.534 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.534 |
0.236 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.551 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.102 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.349 |
|---|
| xy | 0.534 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.178 |
0.083 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.083 |
2.699 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.783 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
16.776 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.096 |
