Jump to
S2C1
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2610.410450 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -2610.413191 |
| HF Energy | -2610.410450 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.067505 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.026 |
1.531 |
0.000 |
| Br2 |
0.026 |
-0.312 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.070 |
1.744 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
| C1 | | 1.8437 | 1.1162 |
Br2 | 1.8437 | | 2.3302 | H3 | 1.1162 | 2.3302 | |
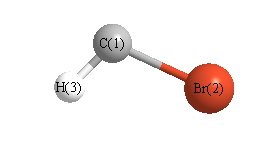 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br2 |
C1 |
H3 |
100.989 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.285 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
0.097 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.188 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.246 |
-0.700 |
0.000 |
1.429 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.771 |
-2.838 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.838 |
-25.289 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.343 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.455 |
-2.838 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.838 |
-1.232 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.687 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.374 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.518 |
|---|
| xy | -2.838 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.825 |
-0.302 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.302 |
6.288 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.332 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
36.981 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.081 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2610.411430 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -2610.414156 |
| HF Energy | -2610.411430 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.916207 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.020 |
1.481 |
0.000 |
| Br2 |
0.020 |
-0.315 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-0.839 |
2.145 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
| C1 | | 1.7958 | 1.0857 |
Br2 | 1.7958 | | 2.6054 | H3 | 1.0857 | 2.6054 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.301 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
0.104 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.197 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.672 |
0.229 |
0.000 |
0.710 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.795 |
-1.629 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.629 |
-21.708 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.883 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.500 |
-1.629 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.629 |
2.632 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.132 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.264 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.088 |
|---|
| xy | -1.629 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.436 |
-0.221 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.221 |
5.941 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.159 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
36.603 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.050 |
