Jump to
S1C2
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/3-21G
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/3-21G
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3PW91/3-21G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -206.719898 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -206.723405 |
| HF Energy | -206.719898 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 101.129950 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/3-21G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3518 |
3381 |
7.32 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3126 |
3005 |
2.61 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3025 |
2907 |
24.50 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2348 |
2257 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1539 |
1479 |
7.80 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1414 |
1359 |
21.36 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1396 |
1341 |
1.57 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1269 |
1220 |
22.15 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1022 |
983 |
22.57 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
987 |
948 |
68.45 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
900 |
865 |
23.90 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
612 |
588 |
2.30 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
464 |
446 |
40.90 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
346 |
333 |
139.35 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
232 |
223 |
6.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11098.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9612) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10667.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/3-21G
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.554 |
0.605 |
0.038 |
| C2 |
0.830 |
0.123 |
0.002 |
| O3 |
-1.528 |
-0.459 |
-0.114 |
| H4 |
-0.693 |
1.192 |
0.959 |
| H5 |
-0.720 |
1.274 |
-0.811 |
| H6 |
-1.424 |
-1.074 |
0.659 |
| N7 |
1.915 |
-0.298 |
-0.019 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
N7 |
| C1 | | 1.4656 | 1.4506 | 1.1011 | 1.0940 | 1.9900 | 2.6298 |
C2 | 1.4656 | | 2.4315 | 2.0927 | 2.0945 | 2.6349 | 1.1645 | O3 | 1.4506 | 2.4315 | | 2.1391 | 2.0358 | 0.9934 | 3.4482 | H4 | 1.1011 | 2.0927 | 2.1391 | | 1.7722 | 2.3996 | 3.1598 | H5 | 1.0940 | 2.0945 | 2.0358 | 1.7722 | | 2.8586 | 3.1691 | H6 | 1.9900 | 2.6349 | 0.9934 | 2.3996 | 2.8586 | | 3.4940 | N7 | 2.6298 | 1.1645 | 3.4482 | 3.1598 | 3.1691 | 3.4940 | |
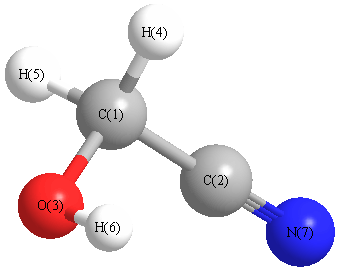 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
N7 |
177.921 |
|
C1 |
O3 |
H6 |
107.547 |
| C2 |
C1 |
O3 |
112.975 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H4 |
108.403 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
108.961 |
|
O3 |
C1 |
H4 |
113.204 |
| O3 |
C1 |
H5 |
105.406 |
|
H4 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.667 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/3-21G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.235 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.332 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.530 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.253 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.294 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.365 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.478 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.059 |
1.142 |
1.513 |
2.798 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-31.522 |
1.240 |
-2.211 |
| y |
1.240 |
-20.293 |
-1.861 |
| z |
-2.211 |
-1.861 |
-21.479 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-10.636 |
1.240 |
-2.211 |
| y |
1.240 |
6.207 |
-1.861 |
| z |
-2.211 |
-1.861 |
4.429 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.857 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -11.229 |
|---|
| xy | 1.240 |
|---|
| xz | -2.211 |
|---|
| yz | -1.861 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.816 |
-0.368 |
-0.041 |
| y |
-0.368 |
3.201 |
-0.202 |
| z |
-0.041 |
-0.202 |
2.654 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
79.534 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.918 |
