Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -581.228626 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -581.228626 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 78.765274 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2275 |
2184 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
945 |
907 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
593 |
569 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Au |
545 |
523 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B1u |
2268 |
2177 |
79.50 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B1u |
864 |
829 |
107.68 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
B2g |
228i |
219i |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
B2u |
2305 |
2213 |
144.76 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
B2u |
357 |
343 |
16.64 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
B3g |
2295 |
2203 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
B3g |
600 |
576 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B3u |
517 |
497 |
0.61 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6666.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9601) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6400.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-31+G**
Point Group is D2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.070 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.070 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
1.254 |
1.856 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
-1.254 |
1.856 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
1.254 |
-1.856 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-1.254 |
-1.856 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| Si1 | | 2.1392 | 1.4798 | 1.4798 | 3.1826 | 3.1826 |
Si2 | 2.1392 | | 3.1826 | 3.1826 | 1.4798 | 1.4798 | H3 | 1.4798 | 3.1826 | | 2.5075 | 3.7114 | 4.4791 | H4 | 1.4798 | 3.1826 | 2.5075 | | 4.4791 | 3.7114 | H5 | 3.1826 | 1.4798 | 3.7114 | 4.4791 | | 2.5075 | H6 | 3.1826 | 1.4798 | 4.4791 | 3.7114 | 2.5075 | |
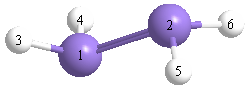 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H5 |
122.088 |
|
Si1 |
Si2 |
H6 |
122.088 |
| Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
122.088 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H4 |
122.088 |
| H3 |
Si1 |
H4 |
115.824 |
|
H5 |
Si2 |
H6 |
115.824 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.048 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.048 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.048 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.048 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-31.716 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-28.940 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-27.536 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.478 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.686 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.792 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 5.584 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.777 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.047 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
6.769 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
14.726 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
70.456 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.394 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -581.229604 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -581.229604 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 78.136798 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2247 |
2158 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
949 |
911 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
570 |
547 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Ag |
307 |
295 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Au |
2276 |
2185 |
176.25 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Au |
528 |
507 |
0.26 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Au |
346 |
332 |
16.97 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
Bg |
2265 |
2174 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
Bg |
612 |
587 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
Bu |
2242 |
2152 |
127.82 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
Bu |
908 |
872 |
165.84 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
Bu |
448 |
430 |
28.68 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6848.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9601) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6575.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-31+G**
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.083 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.083 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
0.404 |
1.803 |
1.234 |
| H4 |
0.404 |
1.803 |
-1.234 |
| H5 |
-0.404 |
-1.803 |
1.234 |
| H6 |
-0.404 |
-1.803 |
-1.234 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| Si1 | | 2.1667 | 1.4852 | 1.4852 | 3.1656 | 3.1656 |
Si2 | 2.1667 | | 3.1656 | 3.1656 | 1.4852 | 1.4852 | H3 | 1.4852 | 3.1656 | | 2.4686 | 3.6965 | 4.4451 | H4 | 1.4852 | 3.1656 | 2.4686 | | 4.4451 | 3.6965 | H5 | 3.1656 | 1.4852 | 3.6965 | 4.4451 | | 2.4686 | H6 | 3.1656 | 1.4852 | 4.4451 | 3.6965 | 2.4686 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H5 |
119.004 |
|
Si1 |
Si2 |
H6 |
119.004 |
| Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
119.004 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H4 |
119.004 |
| H3 |
Si1 |
H4 |
112.425 |
|
H5 |
Si2 |
H6 |
112.425 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.107 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.107 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.053 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.053 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.053 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.053 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-31.504 |
-0.287 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.287 |
-27.692 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-29.241 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.037 |
-0.287 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.287 |
2.680 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.357 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.714 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.812 |
|---|
| xy | -0.287 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.037 |
-0.623 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.623 |
14.962 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.235 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
71.033 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.428 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -581.190988 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -581.190988 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 72.993755 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
2102 |
2018 |
425.93 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
1659 |
1593 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
889 |
853 |
38.73 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
408 |
392 |
1.25 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A1 |
379 |
364 |
0.61 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A2 |
1402 |
1346 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A2 |
636 |
610 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
B1 |
1324 |
1272 |
43.71 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
B1 |
842 |
808 |
13.05 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
B2 |
2073 |
1990 |
12.86 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
B2 |
1379 |
1324 |
1141.26 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B2 |
728 |
699 |
77.58 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6910.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9601) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6634.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-31+G**
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.318 |
-0.089 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.318 |
-0.089 |
| H3 |
-1.031 |
0.000 |
-0.179 |
| H4 |
1.031 |
0.000 |
-0.179 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
1.328 |
1.430 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-1.328 |
1.430 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| Si1 | | 2.6363 | 1.6762 | 1.6762 | 1.5195 | 3.0515 |
Si2 | 2.6363 | | 1.6762 | 1.6762 | 3.0515 | 1.5195 | H3 | 1.6762 | 1.6762 | | 2.0630 | 2.3274 | 2.3274 | H4 | 1.6762 | 1.6762 | 2.0630 | | 2.3274 | 2.3274 | H5 | 1.5195 | 3.0515 | 2.3274 | 2.3274 | | 2.6563 | H6 | 3.0515 | 1.5195 | 2.3274 | 2.3274 | 2.6563 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H5 |
29.864 |
|
Si1 |
Si2 |
H6 |
90.377 |
| Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
38.149 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H4 |
38.149 |
| H3 |
Si1 |
H4 |
75.961 |
|
H5 |
Si2 |
H6 |
60.512 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.230 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.230 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.147 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.147 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.084 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.084 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.802 |
0.802 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.168 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-32.657 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.455 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.888 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-2.345 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.543 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.085 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.489 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.305 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
13.225 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.220 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
78.106 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.838 |
