Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -377.496067 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -377.496067 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 190.704557 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3138 |
3021 |
36.84 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3107 |
2991 |
28.58 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3073 |
2958 |
20.27 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1508 |
1452 |
3.38 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1470 |
1415 |
16.33 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1424 |
1370 |
23.37 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1355 |
1305 |
19.79 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1279 |
1231 |
10.45 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1165 |
1122 |
97.91 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1144 |
1101 |
7.60 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1117 |
1076 |
270.40 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1097 |
1056 |
19.64 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
913 |
879 |
38.39 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
579 |
558 |
4.11 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
476 |
459 |
19.17 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
427 |
411 |
5.17 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
242 |
233 |
8.55 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
119 |
115 |
8.29 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11816.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9627) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11375.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.774 |
-0.586 |
-0.284 |
| C2 |
0.467 |
0.021 |
0.326 |
| F3 |
-1.883 |
0.109 |
0.152 |
| F4 |
1.531 |
-0.765 |
-0.007 |
| F5 |
0.685 |
1.261 |
-0.181 |
| H6 |
-0.713 |
-0.522 |
-1.373 |
| H7 |
-0.865 |
-1.630 |
0.027 |
| H8 |
0.419 |
0.103 |
1.415 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.5105 | 1.3785 | 2.3282 | 2.3562 | 1.0933 | 1.0932 | 2.1873 |
C2 | 1.5105 | | 2.3581 | 1.3633 | 1.3573 | 2.1391 | 2.1422 | 1.0935 | F3 | 1.3785 | 2.3581 | | 3.5267 | 2.8341 | 2.0225 | 2.0187 | 2.6254 | F4 | 2.3282 | 1.3633 | 3.5267 | | 2.2022 | 2.6383 | 2.5467 | 2.0031 | F5 | 2.3562 | 1.3573 | 2.8341 | 2.2022 | | 2.5604 | 3.2869 | 1.9897 | H6 | 1.0933 | 2.1391 | 2.0225 | 2.6383 | 2.5604 | | 1.7925 | 3.0737 | H7 | 1.0932 | 2.1422 | 2.0187 | 2.5467 | 3.2869 | 1.7925 | | 2.5647 | H8 | 2.1873 | 1.0935 | 2.6254 | 2.0031 | 1.9897 | 3.0737 | 2.5647 | |
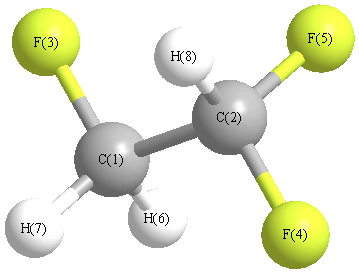 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
F4 |
108.115 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
F5 |
110.382 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
113.310 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F3 |
109.336 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.432 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.683 |
| F3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.271 |
|
F3 |
C1 |
H7 |
108.970 |
| F4 |
C2 |
F5 |
108.082 |
|
F4 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.746 |
| F5 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.073 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.133 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.183 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.263 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
F |
-0.257 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.237 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
F |
-0.226 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.223 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.217 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.235 |
-1.444 |
0.368 |
1.509 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.194 |
1.551 |
1.359 |
| y |
1.551 |
-27.631 |
0.478 |
| z |
1.359 |
0.478 |
-24.565 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.096 |
1.551 |
1.359 |
| y |
1.551 |
0.749 |
0.478 |
| z |
1.359 |
0.478 |
5.347 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 10.695 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.563 |
|---|
| xy | 1.551 |
|---|
| xz | 1.359 |
|---|
| yz | 0.478 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.519 |
-0.024 |
0.021 |
| y |
-0.024 |
3.532 |
0.060 |
| z |
0.021 |
0.060 |
3.422 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
111.312 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.550 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -377.493437 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -377.493437 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 193.387866 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3079 |
2964 |
70.21 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3059 |
2945 |
7.41 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
1505 |
1449 |
6.65 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1447 |
1393 |
20.39 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1424 |
1371 |
30.15 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1190 |
1145 |
132.34 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1110 |
1069 |
26.26 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
877 |
844 |
35.06 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
765 |
736 |
53.19 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
518 |
499 |
12.30 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
231 |
223 |
1.98 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
3119 |
3002 |
26.40 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
1414 |
1361 |
29.74 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
1294 |
1245 |
14.60 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
1147 |
1104 |
112.53 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A" |
960 |
924 |
75.31 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A" |
370 |
357 |
0.17 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A" |
112 |
108 |
2.11 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11809.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9627) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11369.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.735 |
-0.833 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.355 |
0.628 |
0.000 |
| F3 |
-0.386 |
-1.627 |
0.000 |
| F4 |
-0.386 |
0.928 |
1.099 |
| F5 |
-0.386 |
0.928 |
-1.099 |
| H6 |
1.325 |
-1.053 |
-0.895 |
| H7 |
1.325 |
-1.053 |
0.895 |
| H8 |
1.242 |
1.272 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.5094 | 1.3739 | 2.3591 | 2.3591 | 1.0945 | 1.0945 | 2.1651 |
C2 | 1.5094 | | 2.3737 | 1.3588 | 1.3588 | 2.1370 | 2.1370 | 1.0963 | F3 | 1.3739 | 2.3737 | | 2.7815 | 2.7815 | 2.0148 | 2.0148 | 3.3251 | F4 | 2.3591 | 1.3588 | 2.7815 | | 2.1971 | 3.2905 | 2.6256 | 1.9941 | F5 | 2.3591 | 1.3588 | 2.7815 | 2.1971 | | 2.6256 | 3.2905 | 1.9941 | H6 | 1.0945 | 2.1370 | 2.0148 | 3.2905 | 2.6256 | | 1.7902 | 2.4924 | H7 | 1.0945 | 2.1370 | 2.0148 | 2.6256 | 3.2905 | 1.7902 | | 2.4924 | H8 | 2.1651 | 1.0963 | 3.3251 | 1.9941 | 1.9941 | 2.4924 | 2.4924 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
F4 |
110.562 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
F5 |
110.562 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.398 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F3 |
110.738 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.275 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.275 |
| F3 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.899 |
|
F3 |
C1 |
H7 |
108.899 |
| F4 |
C2 |
F5 |
107.895 |
|
F4 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.152 |
| F5 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.152 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.741 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.173 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.268 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
F |
-0.248 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.229 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
F |
-0.229 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.214 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.214 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.184 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
3.127 |
0.095 |
0.000 |
3.128 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.945 |
-0.283 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.283 |
-28.740 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.292 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.571 |
-0.283 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.283 |
-2.122 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.449 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -2.898 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.795 |
|---|
| xy | -0.283 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.502 |
0.004 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.004 |
3.495 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.495 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
103.171 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.157 |
