Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3PW91/3-21G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -157.549657 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -157.560341 |
| HF Energy | -157.549657 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 130.054502 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
|
Au |
129 |
124 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
223 |
214 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
261 |
250 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
263 |
252 |
0.20 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
432 |
414 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
755 |
724 |
8.09 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
842 |
808 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
849 |
815 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
998 |
957 |
5.49 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
1007 |
966 |
3.16 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1030 |
988 |
10.92 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1063 |
1020 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1192 |
1143 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
1236 |
1185 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
1330 |
1276 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1360 |
1304 |
0.18 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
1372 |
1317 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1401 |
1344 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1454 |
1395 |
15.81 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1456 |
1397 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1542 |
1479 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1548 |
1485 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
1560 |
1497 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
1562 |
1498 |
19.88 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
1564 |
1501 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
1566 |
1503 |
14.53 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
3041 |
2918 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
3047 |
2924 |
22.61 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
3050 |
2926 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
3052 |
2928 |
72.06 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
3069 |
2944 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
3091 |
2966 |
5.29 |
|
|
|
|
Bg |
3120 |
2993 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Ag |
3123 |
2996 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
|
Bu |
3124 |
2997 |
64.80 |
|
|
|
|
Au |
3128 |
3001 |
98.35 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29418.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9594) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28224.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/3-21G*
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.430 |
0.639 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.430 |
-0.639 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
0.430 |
1.916 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-0.430 |
-1.916 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.083 |
0.632 |
0.884 |
| H6 |
-1.083 |
0.632 |
-0.884 |
| H7 |
1.083 |
-0.632 |
0.884 |
| H8 |
1.083 |
-0.632 |
-0.884 |
| H9 |
-0.196 |
2.816 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
1.073 |
1.946 |
0.888 |
| H11 |
1.073 |
1.946 |
-0.888 |
| H12 |
0.196 |
-2.816 |
0.000 |
| H13 |
-1.073 |
-1.946 |
0.888 |
| H14 |
-1.073 |
-1.946 |
-0.888 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
| C1 | | 1.5399 | 1.5390 | 2.5548 | 1.0993 | 1.0993 | 2.1643 | 2.1643 | 2.1897 | 2.1806 | 2.1806 | 3.5114 | 2.8077 | 2.8077 |
C2 | 1.5399 | | 2.5548 | 1.5390 | 2.1643 | 2.1643 | 1.0993 | 1.0993 | 3.5114 | 2.8077 | 2.8077 | 2.1897 | 2.1806 | 2.1806 | C3 | 1.5390 | 2.5548 | | 3.9268 | 2.1720 | 2.1720 | 2.7747 | 2.7747 | 1.0965 | 1.0973 | 1.0973 | 4.7377 | 4.2377 | 4.2377 | C4 | 2.5548 | 1.5390 | 3.9268 | | 2.7747 | 2.7747 | 2.1720 | 2.1720 | 4.7377 | 4.2377 | 4.2377 | 1.0965 | 1.0973 | 1.0973 | H5 | 1.0993 | 2.1643 | 2.1720 | 2.7747 | | 1.7684 | 2.5073 | 3.0682 | 2.5177 | 2.5249 | 3.0848 | 3.7824 | 2.5775 | 3.1280 | H6 | 1.0993 | 2.1643 | 2.1720 | 2.7747 | 1.7684 | | 3.0682 | 2.5073 | 2.5177 | 3.0848 | 2.5249 | 3.7824 | 3.1280 | 2.5775 | H7 | 2.1643 | 1.0993 | 2.7747 | 2.1720 | 2.5073 | 3.0682 | | 1.7684 | 3.7824 | 2.5775 | 3.1280 | 2.5177 | 2.5249 | 3.0848 | H8 | 2.1643 | 1.0993 | 2.7747 | 2.1720 | 3.0682 | 2.5073 | 1.7684 | | 3.7824 | 3.1280 | 2.5775 | 2.5177 | 3.0848 | 2.5249 | H9 | 2.1897 | 3.5114 | 1.0965 | 4.7377 | 2.5177 | 2.5177 | 3.7824 | 3.7824 | | 1.7772 | 1.7772 | 5.6460 | 4.9227 | 4.9227 | H10 | 2.1806 | 2.8077 | 1.0973 | 4.2377 | 2.5249 | 3.0848 | 2.5775 | 3.1280 | 1.7772 | | 1.7762 | 4.9227 | 4.4441 | 4.7860 | H11 | 2.1806 | 2.8077 | 1.0973 | 4.2377 | 3.0848 | 2.5249 | 3.1280 | 2.5775 | 1.7772 | 1.7762 | | 4.9227 | 4.7860 | 4.4441 | H12 | 3.5114 | 2.1897 | 4.7377 | 1.0965 | 3.7824 | 3.7824 | 2.5177 | 2.5177 | 5.6460 | 4.9227 | 4.9227 | | 1.7772 | 1.7772 | H13 | 2.8077 | 2.1806 | 4.2377 | 1.0973 | 2.5775 | 3.1280 | 2.5249 | 3.0848 | 4.9227 | 4.4441 | 4.7860 | 1.7772 | | 1.7762 | H14 | 2.8077 | 2.1806 | 4.2377 | 1.0973 | 3.1280 | 2.5775 | 3.0848 | 2.5249 | 4.9227 | 4.7860 | 4.4441 | 1.7772 | 1.7762 | |
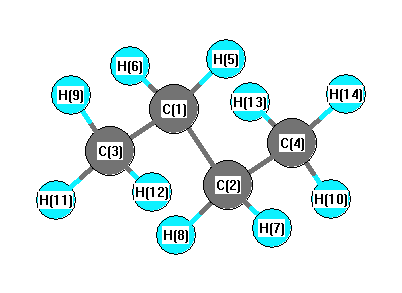 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C4 |
112.148 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.034 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.034 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.257 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
110.492 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H12 |
31.114 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C3 |
112.148 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.034 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.034 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H10 |
17.449 |
| C2 |
C4 |
H13 |
110.492 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H14 |
110.492 |
| C3 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.700 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.700 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.700 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.700 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.089 |
|
H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
107.089 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
108.214 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H12 |
142.371 |
| H10 |
C4 |
H13 |
93.624 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H14 |
113.731 |
| H11 |
C3 |
H12 |
93.212 |
|
H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
108.066 |
Electronic energy levels
Electronic state
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3PW91/3-21G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.422 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.422 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.614 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.614 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.208 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.208 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.208 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.208 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.173 |
-0.221 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.221 |
-28.387 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-27.713 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.123 |
-0.221 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.221 |
-0.444 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.567 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.135 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.214 |
|---|
| xy | -0.221 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.873 |
0.142 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.142 |
6.960 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.751 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
119.176 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.917 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3PW91/3-21G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -157.548606 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 131.957596 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3PW91/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3136 |
3009 |
34.96 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3120 |
2993 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3079 |
2954 |
16.83 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3053 |
2929 |
16.50 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3045 |
2922 |
21.17 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1572 |
1508 |
5.38 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1561 |
1497 |
4.30 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1539 |
1476 |
0.99 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1458 |
1399 |
9.84 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1389 |
1332 |
0.77 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1345 |
1290 |
0.62 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1219 |
1170 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1097 |
1052 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1013 |
972 |
0.49 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
851 |
817 |
0.86 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
804 |
772 |
2.77 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
328 |
315 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
263 |
253 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
110 |
105 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3130 |
3003 |
52.51 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3122 |
2995 |
66.57 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
3087 |
2961 |
17.04 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
3051 |
2927 |
20.90 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
3042 |
2919 |
19.83 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1565 |
1501 |
12.65 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1558 |
1495 |
15.45 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1540 |
1477 |
1.62 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1446 |
1387 |
9.67 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1410 |
1353 |
1.28 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1326 |
1272 |
0.34 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
1177 |
1130 |
4.90 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
1010 |
969 |
6.74 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
969 |
930 |
3.19 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
769 |
738 |
8.69 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
436 |
418 |
1.15 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
214 |
205 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29416.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9594) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28222.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3PW91/3-21G*
Point Group is C2h
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
