Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3710 |
3542 |
95.55 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3268 |
3120 |
0.49 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3201 |
3056 |
14.84 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3192 |
3047 |
15.02 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1684 |
1608 |
67.30 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1646 |
1571 |
81.48 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1554 |
1484 |
25.74 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1506 |
1438 |
3.15 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1452 |
1386 |
60.46 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1432 |
1367 |
24.33 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1387 |
1324 |
62.20 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1334 |
1273 |
12.64 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1326 |
1266 |
15.11 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1297 |
1238 |
34.39 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1217 |
1162 |
7.38 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1153 |
1100 |
5.67 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1100 |
1051 |
12.55 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
952 |
909 |
1.84 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
918 |
876 |
12.91 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
816 |
779 |
15.56 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
663 |
633 |
0.52 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
572 |
546 |
4.33 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
448 |
428 |
12.12 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1014 |
968 |
0.44 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
962 |
919 |
6.11 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
899 |
858 |
3.90 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
839 |
801 |
9.85 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
675 |
644 |
7.05 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
632 |
604 |
21.90 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
545 |
521 |
93.45 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
425 |
405 |
3.25 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
249 |
238 |
0.38 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
237 |
226 |
4.39 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21152.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9547) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20194.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
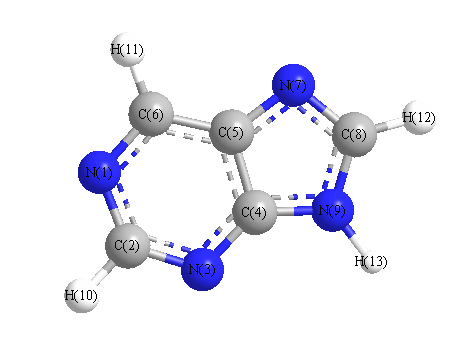
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.297 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.057 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.389 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.469 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.197 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.062 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.358 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
0.025 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
N |
-0.428 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.174 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.304 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.170 |
2.921 |
0.000 |
3.639 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-49.177 |
6.106 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.106 |
-45.984 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-50.673 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.849 |
6.106 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.106 |
3.941 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.092 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.184 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.193 |
|---|
| xy | 6.106 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
14.916 |
1.351 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.351 |
11.557 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.979 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
251.461 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.858 |