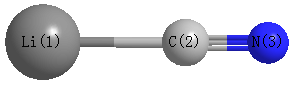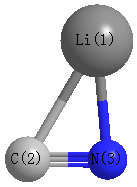Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -100.339332 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -100.338344 |
| HF Energy | -100.339332 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 27.716470 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σ |
2268 |
2165 |
11.66 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σ |
634 |
605 |
109.81 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Π |
154 |
147 |
36.75 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Π |
154 |
147 |
36.75 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1604.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9547) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1531.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.057 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.152 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.012 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 1.9052 | 3.0691 |
C2 | 1.9052 | | 1.1639 | N3 | 3.0691 | 1.1639 | |
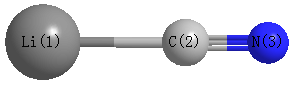 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.208 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.138 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.346 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-8.804 |
8.804 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.079 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-14.079 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.617 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.848 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-7.848 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
15.696 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 31.391 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.689 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.689 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.181 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
25.528 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
5.052 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -100.346456 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -100.345722 |
| HF Energy | -100.346456 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 29.330400 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
1.424 |
-0.599 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.712 |
-0.367 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.571 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 2.1485 | 1.8429 |
C2 | 2.1485 | | 1.1780 | N3 | 1.8429 | 1.1780 | |
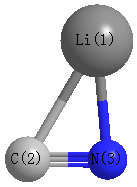 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
58.997 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
87.781 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
33.222 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.232 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.016 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.216 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
6.329 |
-2.428 |
0.000 |
6.779 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-5.762 |
-5.919 |
0.000 |
| y |
-5.919 |
-14.995 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-14.421 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
8.946 |
-5.919 |
0.000 |
| y |
-5.919 |
-4.904 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.042 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -8.084 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 9.234 |
|---|
| xy | -5.919 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.325 |
0.381 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.381 |
3.386 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.792 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
20.617 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.541 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -100.345354 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -100.344245 |
| HF Energy | -100.345354 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 28.448996 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σ |
2173 |
2074 |
165.33 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σ |
738 |
705 |
139.90 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Π |
104 |
99 |
25.67 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Π |
104 |
99 |
25.67 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1558.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9547) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1488.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.871 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.065 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.111 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 2.9367 | 1.7603 |
C2 | 2.9367 | | 1.1764 | N3 | 1.7603 | 1.1764 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.375 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.279 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.095 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.598 |
8.598 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.120 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-14.120 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.800 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.160 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-6.160 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
12.319 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 24.639 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.646 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.646 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.198 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
23.656 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.864 |