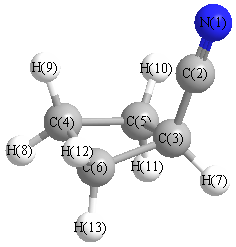
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3176 |
3032 |
31.13 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3154 |
3011 |
8.37 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3107 |
2967 |
2.38 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3101 |
2961 |
2.05 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3096 |
2956 |
25.60 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
2381 |
2273 |
16.79 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1512 |
1444 |
0.92 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1487 |
1420 |
3.79 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1361 |
1300 |
2.19 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1286 |
1228 |
0.67 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1245 |
1189 |
0.24 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1130 |
1079 |
2.10 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1096 |
1046 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
979 |
935 |
0.64 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
910 |
868 |
1.68 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
757 |
723 |
1.40 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
588 |
562 |
1.45 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
538 |
514 |
0.48 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
268 |
256 |
2.11 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
127 |
121 |
2.97 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3167 |
3024 |
11.67 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3103 |
2963 |
39.91 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
1479 |
1412 |
1.99 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1284 |
1226 |
1.74 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1261 |
1204 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1247 |
1190 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1216 |
1161 |
0.28 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1047 |
1000 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
966 |
922 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
956 |
913 |
2.10 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
789 |
753 |
1.31 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
553 |
528 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
182 |
174 |
4.98 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24276.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9547) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23176.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.350 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.296 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.186 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.276 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.270 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.270 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.916 |
-3.043 |
0.000 |
4.215 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-38.868 |
-6.529 |
0.000 |
| y |
-6.529 |
-41.954 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-34.767 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.507 |
-6.529 |
0.000 |
| y |
-6.529 |
-5.137 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.644 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 11.288 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.086 |
|---|
| xy | -6.529 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.000 |
1.743 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.743 |
8.849 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.113 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
155.430 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.467 |