Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3209 |
3054 |
2.41 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3171 |
3018 |
16.37 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3158 |
3005 |
29.27 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3141 |
2988 |
11.39 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3133 |
2981 |
1.27 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3121 |
2970 |
1.39 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3078 |
2929 |
28.08 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3075 |
2926 |
4.99 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1523 |
1449 |
8.06 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1514 |
1440 |
7.69 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1498 |
1425 |
5.49 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1491 |
1419 |
4.96 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1433 |
1364 |
3.82 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1417 |
1348 |
0.66 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1353 |
1287 |
4.49 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1339 |
1274 |
4.15 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1312 |
1249 |
8.79 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1261 |
1200 |
10.95 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1220 |
1161 |
11.63 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1146 |
1091 |
1.27 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1114 |
1060 |
1.77 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1082 |
1029 |
3.69 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1057 |
1005 |
1.02 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
961 |
914 |
11.90 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
849 |
808 |
8.71 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
825 |
785 |
7.87 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
760 |
723 |
57.55 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
678 |
645 |
38.12 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
466 |
443 |
2.06 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
390 |
371 |
1.63 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
300 |
285 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
244 |
232 |
0.55 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
221 |
210 |
2.94 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
191 |
181 |
3.87 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
117 |
111 |
3.80 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
97 |
92 |
1.41 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25470.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9515) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24235.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
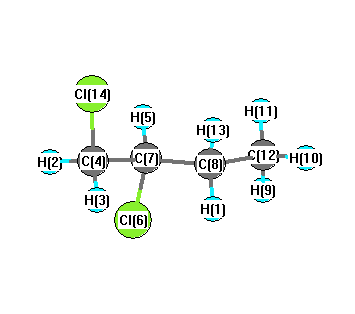
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.206 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.198 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.343 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Cl |
-0.067 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
-0.239 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.235 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.156 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.141 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.136 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
C |
-0.401 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.165 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Cl |
-0.065 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.326 |
0.649 |
0.241 |
0.765 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-57.176 |
3.516 |
-0.297 |
| y |
3.516 |
-50.501 |
-0.205 |
| z |
-0.297 |
-0.205 |
-50.045 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.903 |
3.516 |
-0.297 |
| y |
3.516 |
3.110 |
-0.205 |
| z |
-0.297 |
-0.205 |
3.793 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 7.586 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -6.675 |
|---|
| xy | 3.516 |
|---|
| xz | -0.297 |
|---|
| yz | -0.205 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
321.443 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
17.929 |