Vibrational Frequencies calculated at mPW1PW91/6-31G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3305 |
3128 |
4.42 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3190 |
3020 |
13.59 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3175 |
3006 |
36.38 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3149 |
2981 |
12.68 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3117 |
2950 |
47.01 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3100 |
2935 |
18.05 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3078 |
2914 |
21.27 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3066 |
2902 |
48.73 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1776 |
1681 |
45.27 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1568 |
1484 |
0.75 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1549 |
1466 |
1.03 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1539 |
1456 |
8.82 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1522 |
1441 |
11.09 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1471 |
1392 |
13.99 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1415 |
1340 |
8.16 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1353 |
1281 |
8.60 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1301 |
1232 |
48.26 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1277 |
1209 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1241 |
1175 |
43.04 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1219 |
1154 |
0.92 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1117 |
1058 |
5.79 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1102 |
1043 |
2.60 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1072 |
1014 |
6.53 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1045 |
989 |
12.56 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
987 |
934 |
53.43 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
949 |
899 |
15.54 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
898 |
850 |
26.64 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
862 |
816 |
0.58 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
773 |
732 |
32.94 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
742 |
702 |
0.94 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
643 |
609 |
1.44 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
557 |
527 |
1.21 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
335 |
317 |
3.12 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
228 |
216 |
10.62 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
159 |
151 |
1.93 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
39 |
37 |
2.77 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26958.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9466) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25518.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
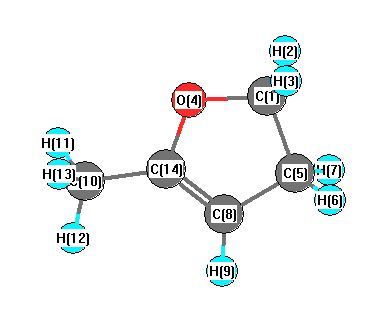
Charges from optimized geometry at mPW1PW91/6-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.076 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.563 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.399 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.178 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.178 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.201 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.165 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
C |
-0.532 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.194 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.178 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.194 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.318 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.604 |
1.078 |
0.001 |
1.235 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.900 |
1.435 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.435 |
-37.859 |
-0.001 |
| z |
0.000 |
-0.001 |
-37.052 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.555 |
1.435 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.435 |
-3.883 |
-0.001 |
| z |
0.000 |
-0.001 |
-2.672 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.345 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.958 |
|---|
| xy | 1.435 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | -0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.407 |
-0.591 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.591 |
8.122 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.454 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
157.868 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.565 |