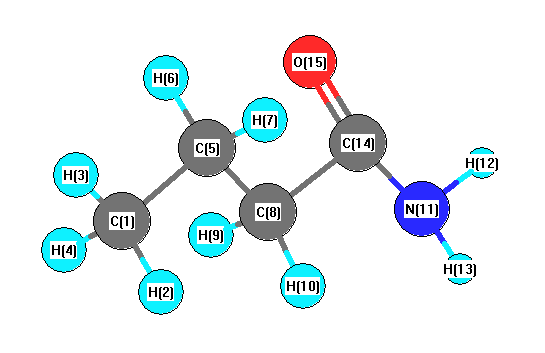
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at LSDA/STO-3G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3857 |
3454 |
8.37 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3637 |
3257 |
23.47 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3465 |
3103 |
0.38 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3461 |
3099 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3423 |
3066 |
0.41 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3402 |
3047 |
4.69 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3309 |
2964 |
4.24 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3293 |
2949 |
1.44 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3242 |
2903 |
33.46 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1881 |
1685 |
76.85 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1666 |
1492 |
39.60 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1659 |
1486 |
5.75 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1650 |
1477 |
6.52 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1641 |
1470 |
2.57 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1606 |
1439 |
4.39 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1535 |
1375 |
2.07 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1467 |
1314 |
1.48 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1407 |
1260 |
17.73 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1326 |
1187 |
114.52 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1307 |
1171 |
11.70 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1299 |
1163 |
5.41 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1203 |
1077 |
20.60 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1160 |
1039 |
9.83 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1148 |
1028 |
3.08 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1086 |
972 |
3.75 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
985 |
882 |
7.60 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
945 |
846 |
2.38 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
879 |
787 |
7.39 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
810 |
725 |
12.06 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
600 |
538 |
6.78 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
578 |
517 |
8.76 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
471 |
422 |
11.95 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
422 |
378 |
1.63 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
357 |
319 |
6.21 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
267 |
239 |
3.69 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
236 |
211 |
228.81 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
189 |
169 |
12.55 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
110 |
98 |
6.43 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
22 |
20 |
1.03 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30499.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8955) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27312.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.276 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.089 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.088 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.177 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.087 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.104 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.197 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.093 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.093 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.382 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.216 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.211 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.171 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.211 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.241 |
-2.486 |
-0.642 |
2.852 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.838 |
3.368 |
2.076 |
| y |
3.368 |
-34.648 |
0.688 |
| z |
2.076 |
0.688 |
-34.197 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.584 |
3.368 |
2.076 |
| y |
3.368 |
-3.130 |
0.688 |
| z |
2.076 |
0.688 |
-2.454 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.909 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.809 |
|---|
| xy | 3.368 |
|---|
| xz | 2.076 |
|---|
| yz | 0.688 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.306 |
0.367 |
0.194 |
| y |
0.367 |
4.588 |
-0.042 |
| z |
0.194 |
-0.042 |
2.661 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
0.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
0.000 |