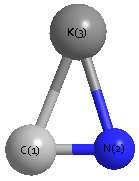Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at LSDA/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -690.847913 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -690.847320 |
| HF Energy | -690.847913 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 61.400701 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at LSDA/6-31G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.294 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.258 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.435 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.5524 | 3.7289 |
C2 | 2.5524 | | 1.1765 | N3 | 3.7289 | 1.1765 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.619 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.226 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.393 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.367 |
11.367 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.253 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.253 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-29.723 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.235 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.235 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-6.471 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -12.941 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.717 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.717 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.951 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
98.687 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.934 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at LSDA/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -690.846938 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -690.846938 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.819018 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at LSDA/6-31G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.199 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.391 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.206 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.5903 | 2.4054 |
C2 | 3.5903 | | 1.1849 | N3 | 2.4054 | 1.1849 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.656 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.149 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.507 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.385 |
11.385 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.354 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.354 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-31.935 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.291 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.291 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-8.582 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -17.164 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.827 |
-0.000 |
-0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
3.826 |
-0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
-0.000 |
8.242 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
88.185 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.391 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at LSDA/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -690.856057 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -690.856020 |
| HF Energy | -690.856057 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 69.587839 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at LSDA/6-31G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.017 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.636 |
-1.535 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.545 |
-1.445 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.6307 | 2.5225 |
C2 | 2.6307 | | 1.1850 | N3 | 2.5225 | 1.1850 | |
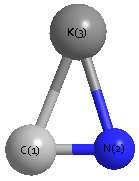 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
71.660 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
81.858 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
26.482 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.576 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.146 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.430 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.467 |
9.323 |
0.000 |
9.335 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.449 |
0.526 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.526 |
-25.358 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.537 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.001 |
0.526 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.526 |
0.135 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.866 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 5.733 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.091 |
|---|
| xy | 0.526 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.786 |
-0.032 |
-0.000 |
| y |
-0.032 |
5.101 |
0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
3.802 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
68.839 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.297 |