Vibrational Frequencies calculated at LSDA/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3580 |
3516 |
26.75 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3445 |
3383 |
23.23 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3065 |
3010 |
19.90 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3057 |
3002 |
28.93 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3032 |
2977 |
1.83 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3010 |
2956 |
10.32 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2993 |
2939 |
14.62 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2975 |
2921 |
17.71 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
2958 |
2905 |
6.61 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1752 |
1720 |
172.64 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1599 |
1570 |
113.82 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1506 |
1479 |
13.42 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1500 |
1473 |
14.24 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1493 |
1466 |
6.42 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1448 |
1422 |
11.68 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1401 |
1376 |
3.98 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1376 |
1351 |
127.01 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1344 |
1320 |
5.74 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1304 |
1280 |
47.51 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1260 |
1237 |
2.12 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1232 |
1210 |
0.91 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1137 |
1117 |
5.61 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1106 |
1086 |
6.45 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1088 |
1069 |
3.74 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1062 |
1043 |
0.53 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
937 |
920 |
5.59 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
893 |
877 |
3.74 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
836 |
821 |
10.47 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
758 |
744 |
28.14 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
691 |
679 |
58.98 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
611 |
600 |
26.07 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
536 |
527 |
167.53 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
512 |
503 |
43.35 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
428 |
420 |
1.80 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
357 |
351 |
3.72 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
256 |
251 |
1.00 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
196 |
192 |
9.12 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
87 |
86 |
1.74 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
76 |
74 |
2.79 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28447.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.982) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27935.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
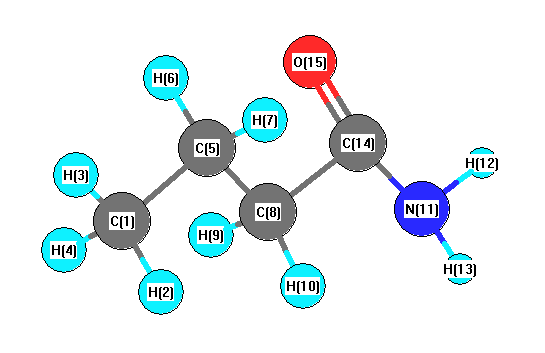
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/3-21G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.634 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.215 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.420 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.217 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.241 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.516 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.207 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.241 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.739 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.327 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.321 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.575 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.447 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.037 |
-3.459 |
-0.189 |
3.616 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.948 |
-5.618 |
-0.532 |
| y |
-5.618 |
-38.252 |
-0.037 |
| z |
-0.532 |
-0.037 |
-37.639 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.998 |
-5.618 |
-0.532 |
| y |
-5.618 |
-3.959 |
-0.037 |
| z |
-0.532 |
-0.037 |
-3.038 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.077 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 7.305 |
|---|
| xy | -5.618 |
|---|
| xz | -0.532 |
|---|
| yz | -0.037 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.786 |
-0.446 |
-0.106 |
| y |
-0.446 |
7.469 |
0.098 |
| z |
-0.106 |
0.098 |
5.193 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
0.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
0.000 |