Vibrational Frequencies calculated at LSDA/6-31G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3129 |
3066 |
2.62 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3110 |
3047 |
7.06 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3083 |
3020 |
9.92 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3053 |
2991 |
13.31 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3047 |
2985 |
1.71 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3032 |
2971 |
1.79 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2991 |
2930 |
10.19 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2983 |
2923 |
3.39 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1475 |
1445 |
10.17 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1468 |
1438 |
13.35 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1463 |
1433 |
14.83 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1449 |
1420 |
2.32 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1398 |
1369 |
23.53 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1369 |
1341 |
19.80 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1315 |
1288 |
9.28 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1293 |
1267 |
5.66 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1251 |
1226 |
9.54 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1242 |
1217 |
26.73 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1176 |
1152 |
17.64 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1136 |
1113 |
7.07 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1114 |
1092 |
3.46 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1091 |
1069 |
9.70 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1028 |
1007 |
18.40 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
955 |
936 |
3.80 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
924 |
906 |
7.23 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
786 |
770 |
11.29 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
727 |
712 |
34.55 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
581 |
569 |
31.56 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
433 |
424 |
2.79 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
401 |
393 |
8.45 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
330 |
324 |
5.88 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
253 |
248 |
0.53 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
239 |
235 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
147 |
144 |
3.12 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
121 |
118 |
1.83 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
74 |
72 |
4.35 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24833.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9797) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24329.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
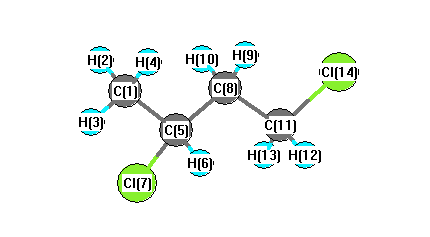
Charges from optimized geometry at LSDA/6-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.478 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.196 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.200 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.185 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.353 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.221 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Cl |
-0.039 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.271 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.200 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.208 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
C |
-0.519 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.221 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.247 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Cl |
-0.018 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.637 |
2.129 |
1.204 |
2.943 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-60.435 |
-4.689 |
0.215 |
| y |
-4.689 |
-50.992 |
-0.092 |
| z |
0.215 |
-0.092 |
-50.124 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-9.877 |
-4.689 |
0.215 |
| y |
-4.689 |
4.288 |
-0.092 |
| z |
0.215 |
-0.092 |
5.590 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 11.179 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -9.444 |
|---|
| xy | -4.689 |
|---|
| xz | 0.215 |
|---|
| yz | -0.092 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
11.260 |
0.563 |
-0.326 |
| y |
0.563 |
9.237 |
0.245 |
| z |
-0.326 |
0.245 |
6.956 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
0.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
0.000 |