Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at SVWN/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.038197 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.042182 |
| HF Energy | -169.038197 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.015358 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at SVWN/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3756 |
3717 |
73.43 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3477 |
3441 |
14.70 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
2911 |
2881 |
77.65 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1761 |
1743 |
195.10 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1373 |
1358 |
13.01 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1292 |
1279 |
169.93 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1152 |
1140 |
26.48 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1026 |
1015 |
235.21 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
614 |
607 |
1.82 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
999 |
989 |
2.86 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
804 |
795 |
73.40 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
421 |
417 |
65.24 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9792.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9896) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9690.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at SVWN/6-311G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.371 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-0.999 |
-0.526 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.192 |
-0.024 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.345 |
1.427 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.846 |
-0.053 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.836 |
0.772 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3424 | 1.2559 | 1.1106 | 1.8945 | 1.8790 |
O2 | 1.3424 | | 2.2474 | 2.0592 | 0.9710 | 3.1174 | N3 | 1.2559 | 2.2474 | | 2.1139 | 3.0386 | 1.0238 | H4 | 1.1106 | 2.0592 | 2.1139 | | 2.1078 | 2.2772 | H5 | 1.8945 | 0.9710 | 3.0386 | 2.1078 | | 3.7735 | H6 | 1.8790 | 3.1174 | 1.0238 | 2.2772 | 3.7735 | |
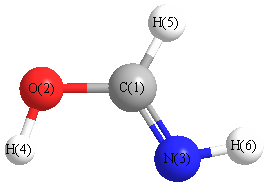 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
108.895 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
110.610 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
119.712 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
113.829 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
126.459 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at SVWN/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.056 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.251 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.343 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.091 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.257 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.190 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.049 |
3.106 |
0.000 |
3.721 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-13.601 |
1.307 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.307 |
-17.972 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.816 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.793 |
1.307 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.307 |
-1.764 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.029 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.058 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.371 |
|---|
| xy | 1.307 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.123 |
-0.042 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.042 |
3.147 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.839 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.992 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.403 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at SVWN/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.049217 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.053356 |
| HF Energy | -169.049217 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.425714 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at SVWN/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3602 |
3564 |
39.31 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3472 |
3436 |
12.51 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3011 |
2980 |
33.54 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1730 |
1712 |
244.10 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1352 |
1338 |
19.05 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1334 |
1320 |
1.31 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1163 |
1151 |
144.01 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1039 |
1028 |
138.40 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
572 |
566 |
59.05 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1008 |
998 |
1.99 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
807 |
799 |
15.67 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
668 |
661 |
199.35 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9879.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9896) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9776.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at SVWN/6-311G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.418 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.107 |
-0.322 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.145 |
-0.109 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.261 |
1.490 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.789 |
-1.252 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.890 |
0.594 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3320 | 1.2607 | 1.1036 | 1.8470 | 1.8986 |
O2 | 1.3320 | | 2.2627 | 2.0005 | 0.9822 | 3.1345 | N3 | 1.2607 | 2.2627 | | 2.1296 | 2.2472 | 1.0239 | H4 | 1.1036 | 2.0005 | 2.1296 | | 2.7925 | 2.3309 | H5 | 1.8470 | 0.9822 | 2.2472 | 2.7925 | | 3.2538 | H6 | 1.8986 | 3.1345 | 1.0239 | 2.3309 | 3.2538 | |
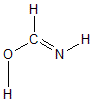 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
104.898 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
111.990 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
121.526 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
110.093 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
128.381 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at SVWN/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.085 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.268 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.397 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.129 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.252 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.156 |
0.939 |
0.000 |
0.952 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.179 |
3.294 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.294 |
-14.289 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.817 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.626 |
3.294 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.294 |
4.709 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.083 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.166 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.889 |
|---|
| xy | 3.294 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.540 |
0.117 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.117 |
3.627 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.828 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.244 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.344 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at SVWN/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.042966 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.047045 |
| HF Energy | -169.042966 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.944945 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at SVWN/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3657 |
3619 |
23.79 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3366 |
3331 |
5.55 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3070 |
3038 |
8.80 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1733 |
1715 |
258.20 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1352 |
1338 |
0.17 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1298 |
1285 |
29.53 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1103 |
1091 |
192.86 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1044 |
1033 |
106.40 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
572 |
566 |
38.90 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1027 |
1016 |
77.71 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
827 |
818 |
54.99 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
562 |
556 |
68.59 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9805.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9896) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9703.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at SVWN/6-311G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.435 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.097 |
-0.342 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.219 |
0.117 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.300 |
1.492 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.817 |
-1.278 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.364 |
-0.905 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3441 | 1.2596 | 1.0994 | 1.8974 | 1.9122 |
O2 | 1.3441 | | 2.3610 | 1.9998 | 0.9777 | 2.5253 | N3 | 1.2596 | 2.3610 | | 2.0492 | 2.4674 | 1.0323 | H4 | 1.0994 | 1.9998 | 2.0492 | | 2.8182 | 2.9186 | H5 | 1.8974 | 0.9777 | 2.4674 | 2.8182 | | 2.2124 | H6 | 1.9122 | 2.5253 | 1.0323 | 2.9186 | 2.2124 | |
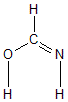 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
108.585 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
112.720 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
130.106 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.441 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
120.453 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at SVWN/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.059 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.266 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.354 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.238 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.163 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.984 |
-1.961 |
0.000 |
2.194 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.878 |
-1.831 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.831 |
-13.052 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.802 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.951 |
-1.831 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.831 |
7.788 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.837 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.674 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -9.826 |
|---|
| xy | -1.831 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.322 |
-0.111 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.111 |
3.801 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.859 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.886 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.394 |


