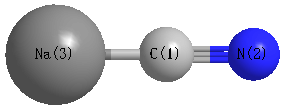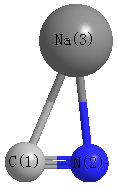Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at SVWN/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -253.999625 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -253.999064 |
| HF Energy | -253.999625 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 47.012391 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at SVWN/6-311G*
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.670 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.836 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.534 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1655 | 2.2036 |
N2 | 1.1655 | | 3.3691 | Na3 | 2.2036 | 3.3691 | |
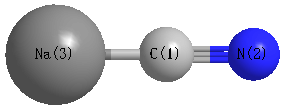 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at SVWN/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.332 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.289 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.621 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.052 |
10.052 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.308 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.308 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-13.509 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.899 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-1.899 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.799 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 7.598 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.871 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.871 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.220 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
62.168 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.885 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at SVWN/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -254.004005 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -254.003799 |
| HF Energy | -254.004005 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 52.467776 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at SVWN/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.107 |
0.663 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.066 |
0.000 |
| Na3 |
-0.604 |
-1.040 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1779 | 2.4139 |
N2 | 1.1779 | | 2.1914 | Na3 | 2.4139 | 2.1914 | |
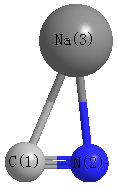 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
85.970 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
29.127 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
64.903 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at SVWN/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.173 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.349 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.522 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-4.438 |
-6.885 |
0.000 |
8.192 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.608 |
3.532 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.532 |
-14.396 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-17.476 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.672 |
3.532 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.532 |
4.146 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.474 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.948 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.212 |
|---|
| xy | 3.532 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.190 |
0.093 |
-0.000 |
| y |
0.093 |
3.950 |
0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
3.045 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
43.485 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.594 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at SVWN/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -253.999127 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -253.998331 |
| HF Energy | -253.999127 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 49.229485 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at SVWN/6-311G*
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.835 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.659 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.420 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1754 | 3.2552 |
N2 | 1.1754 | | 2.0798 | Na3 | 3.2552 | 2.0798 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at SVWN/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.228 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.440 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.668 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.355 |
10.355 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.274 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.274 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-16.177 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.548 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.548 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.097 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.194 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.814 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.814 |
-0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
-0.000 |
6.591 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
55.997 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.483 |