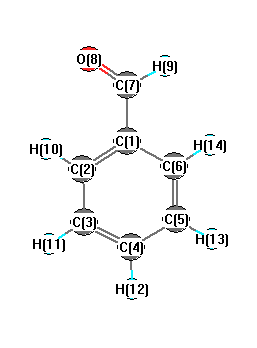
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3228 |
3104 |
8.53 |
266.23 |
0.09 |
0.17 |
| 2 |
A' |
3222 |
3098 |
7.82 |
65.99 |
0.16 |
0.28 |
| 3 |
A' |
3212 |
3089 |
8.49 |
82.09 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
| 4 |
A' |
3201 |
3078 |
0.90 |
79.93 |
0.69 |
0.82 |
| 5 |
A' |
3190 |
3068 |
3.13 |
46.57 |
0.39 |
0.56 |
| 6 |
A' |
2924 |
2812 |
105.58 |
142.40 |
0.28 |
0.44 |
| 7 |
A' |
1799 |
1730 |
287.96 |
114.36 |
0.35 |
0.52 |
| 8 |
A' |
1671 |
1607 |
30.88 |
92.62 |
0.56 |
0.71 |
| 9 |
A' |
1654 |
1590 |
12.08 |
10.86 |
0.56 |
0.72 |
| 10 |
A' |
1520 |
1462 |
1.54 |
1.16 |
0.49 |
0.66 |
| 11 |
A' |
1482 |
1425 |
13.17 |
1.98 |
0.32 |
0.49 |
| 12 |
A' |
1410 |
1356 |
6.93 |
2.61 |
0.58 |
0.74 |
| 13 |
A' |
1391 |
1337 |
8.34 |
0.46 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 14 |
A' |
1321 |
1270 |
15.19 |
1.46 |
0.29 |
0.45 |
| 15 |
A' |
1237 |
1189 |
61.65 |
32.26 |
0.18 |
0.30 |
| 16 |
A' |
1180 |
1134 |
15.40 |
7.93 |
0.14 |
0.25 |
| 17 |
A' |
1174 |
1129 |
1.49 |
6.22 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 18 |
A' |
1102 |
1059 |
5.95 |
1.16 |
0.08 |
0.14 |
| 19 |
A' |
1051 |
1010 |
2.94 |
22.93 |
0.04 |
0.07 |
| 20 |
A' |
1013 |
974 |
0.13 |
28.13 |
0.04 |
0.07 |
| 21 |
A' |
844 |
811 |
31.24 |
13.42 |
0.06 |
0.11 |
| 22 |
A' |
658 |
633 |
23.32 |
2.85 |
0.29 |
0.45 |
| 23 |
A' |
622 |
598 |
0.56 |
4.43 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
| 24 |
A' |
442 |
425 |
0.21 |
5.93 |
0.21 |
0.34 |
| 25 |
A' |
216 |
208 |
8.28 |
0.59 |
0.43 |
0.61 |
| 26 |
A" |
1037 |
997 |
1.25 |
1.45 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 27 |
A" |
1010 |
971 |
0.02 |
0.05 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 28 |
A" |
998 |
959 |
0.00 |
0.05 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 29 |
A" |
943 |
907 |
1.31 |
0.52 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 30 |
A" |
864 |
831 |
0.00 |
0.30 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 31 |
A" |
764 |
734 |
41.64 |
0.33 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 32 |
A" |
706 |
679 |
36.33 |
0.02 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 33 |
A" |
468 |
450 |
7.48 |
0.15 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 34 |
A" |
417 |
401 |
0.11 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 35 |
A" |
239 |
230 |
7.65 |
0.83 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 36 |
A" |
121 |
116 |
4.60 |
1.23 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24162.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9616) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23235.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBE1PBE/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
1.721 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.396 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.454 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.293 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.352 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
0.316 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
0.719 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
O |
-0.617 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
-0.389 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
-0.751 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
-0.584 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
-0.570 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
-0.588 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
-0.751 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.334 |
-2.560 |
0.000 |
3.464 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-44.651 |
6.433 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.433 |
-47.223 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-49.335 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.628 |
6.433 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.433 |
-0.230 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.398 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.796 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.572 |
|---|
| xy | 6.433 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
14.181 |
-1.221 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.221 |
16.850 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.379 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
262.073 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
16.189 |