Jump to
S1C2
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/6-311G*
Geometric Data calculated at PBE1PBE/6-311G*
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at PBE1PBE/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -235.593707 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -235.607115 |
| HF Energy | -235.593707 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 250.165314 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3119 |
2990 |
135.95 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3112 |
2983 |
17.91 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3107 |
2978 |
32.56 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3075 |
2947 |
18.37 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3061 |
2934 |
10.72 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3056 |
2929 |
6.92 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
3039 |
2913 |
39.07 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
3038 |
2912 |
26.29 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1516 |
1453 |
13.04 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1510 |
1447 |
3.92 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1504 |
1441 |
1.96 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1422 |
1363 |
13.62 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1421 |
1362 |
2.19 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1391 |
1333 |
0.38 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1374 |
1317 |
7.92 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1286 |
1233 |
4.34 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1264 |
1212 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1209 |
1158 |
0.20 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1155 |
1107 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
1062 |
1018 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
968 |
928 |
1.04 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
955 |
916 |
0.92 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
878 |
841 |
1.25 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A' |
818 |
784 |
1.41 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A' |
651 |
624 |
1.81 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A' |
428 |
410 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A' |
326 |
313 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A' |
97 |
93 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
3115 |
2986 |
42.15 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
3112 |
2983 |
31.29 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
3109 |
2980 |
9.80 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
3054 |
2927 |
81.71 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
1512 |
1449 |
6.67 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
1510 |
1447 |
0.39 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
1480 |
1419 |
6.99 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
1300 |
1246 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
1279 |
1226 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
1236 |
1184 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
1152 |
1105 |
0.60 |
|
|
|
| 40 |
A" |
1140 |
1093 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 41 |
A" |
1004 |
962 |
4.25 |
|
|
|
| 42 |
A" |
925 |
887 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 43 |
A" |
916 |
878 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 44 |
A" |
812 |
778 |
0.27 |
|
|
|
| 45 |
A" |
375 |
359 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 46 |
A" |
261 |
251 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
| 47 |
A" |
256 |
246 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 48 |
A" |
235 |
226 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 36811.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9585) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 35283.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBE1PBE/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.256 |
0.085 |
1.078 |
| C2 |
0.256 |
0.085 |
-1.078 |
| C3 |
-0.659 |
0.711 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
0.849 |
-0.855 |
0.000 |
| C5 |
-0.859 |
2.212 |
0.000 |
| C6 |
0.256 |
-2.252 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
0.993 |
0.805 |
1.448 |
| H8 |
-0.229 |
-0.387 |
1.938 |
| H9 |
0.993 |
0.805 |
-1.448 |
| H10 |
-0.229 |
-0.387 |
-1.938 |
| H11 |
-1.635 |
0.212 |
0.000 |
| H12 |
1.942 |
-0.922 |
0.000 |
| H13 |
0.104 |
2.734 |
0.000 |
| H14 |
-0.839 |
-2.221 |
0.000 |
| H15 |
-1.415 |
2.539 |
-0.884 |
| H16 |
-1.415 |
2.539 |
0.884 |
| H17 |
0.571 |
-2.814 |
-0.885 |
| H18 |
0.571 |
-2.814 |
0.885 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
H16 |
H17 |
H18 |
| C1 | | 2.1554 | 1.5460 | 1.5483 | 2.6318 | 2.5738 | 1.0949 | 1.0945 | 2.7276 | 3.0907 | 2.1796 | 2.2403 | 2.8635 | 2.7712 | 3.5586 | 2.9752 | 3.5150 | 2.9224 |
C2 | 2.1554 | | 1.5460 | 1.5483 | 2.6318 | 2.5738 | 2.7276 | 3.0907 | 1.0949 | 1.0945 | 2.1796 | 2.2403 | 2.8635 | 2.7712 | 2.9752 | 3.5586 | 2.9224 | 3.5150 | C3 | 1.5460 | 1.5460 | | 2.1742 | 1.5141 | 3.1012 | 2.1988 | 2.2688 | 2.1988 | 2.2688 | 1.0956 | 3.0711 | 2.1620 | 2.9378 | 2.1670 | 2.1670 | 3.8369 | 3.8369 | C4 | 1.5483 | 1.5483 | 2.1742 | | 3.5103 | 1.5182 | 2.2070 | 2.2664 | 2.2070 | 2.2664 | 2.7035 | 1.0946 | 3.6651 | 2.1722 | 4.1748 | 4.1748 | 2.1675 | 2.1675 | C5 | 2.6318 | 2.6318 | 1.5141 | 3.5103 | | 4.6011 | 2.7396 | 3.3029 | 2.7396 | 3.3029 | 2.1449 | 4.2029 | 1.0952 | 4.4333 | 1.0949 | 1.0949 | 5.2996 | 5.2996 | C6 | 2.5738 | 2.5738 | 3.1012 | 1.5182 | 4.6011 | | 3.4619 | 2.7328 | 3.4619 | 2.7328 | 3.1060 | 2.1476 | 4.9882 | 1.0953 | 5.1508 | 5.1508 | 1.0946 | 1.0946 | H7 | 1.0949 | 2.7276 | 2.1988 | 2.2070 | 2.7396 | 3.4619 | | 1.7761 | 2.8956 | 3.7918 | 3.0582 | 2.4450 | 2.5704 | 3.8224 | 3.7745 | 3.0209 | 4.3260 | 3.6863 | H8 | 1.0945 | 3.0907 | 2.2688 | 2.2664 | 3.3029 | 2.7328 | 1.7761 | | 3.7918 | 3.8760 | 2.4682 | 2.9585 | 3.6889 | 2.7371 | 4.2353 | 3.3291 | 3.8075 | 2.7635 | H9 | 2.7276 | 1.0949 | 2.1988 | 2.2070 | 2.7396 | 3.4619 | 2.8956 | 3.7918 | | 1.7761 | 3.0582 | 2.4450 | 2.5704 | 3.8224 | 3.0209 | 3.7745 | 3.6863 | 4.3260 | H10 | 3.0907 | 1.0945 | 2.2688 | 2.2664 | 3.3029 | 2.7328 | 3.7918 | 3.8760 | 1.7761 | | 2.4682 | 2.9585 | 3.6889 | 2.7371 | 3.3291 | 4.2353 | 2.7635 | 3.8075 | H11 | 2.1796 | 2.1796 | 1.0956 | 2.7035 | 2.1449 | 3.1060 | 3.0582 | 2.4682 | 3.0582 | 2.4682 | | 3.7520 | 3.0629 | 2.5603 | 2.4989 | 2.4989 | 3.8480 | 3.8480 | H12 | 2.2403 | 2.2403 | 3.0711 | 1.0946 | 4.2029 | 2.1476 | 2.4450 | 2.9585 | 2.4450 | 2.9585 | 3.7520 | | 4.0916 | 3.0695 | 4.9022 | 4.9022 | 2.4980 | 2.4980 | H13 | 2.8635 | 2.8635 | 2.1620 | 3.6651 | 1.0952 | 4.9882 | 2.5704 | 3.6889 | 2.5704 | 3.6889 | 3.0629 | 4.0916 | | 5.0440 | 1.7687 | 1.7687 | 5.6371 | 5.6371 | H14 | 2.7712 | 2.7712 | 2.9378 | 2.1722 | 4.4333 | 1.0953 | 3.8224 | 2.7371 | 3.8224 | 2.7371 | 2.5603 | 3.0695 | 5.0440 | | 4.8760 | 4.8760 | 1.7675 | 1.7675 | H15 | 3.5586 | 2.9752 | 2.1670 | 4.1748 | 1.0949 | 5.1508 | 3.7745 | 4.2353 | 3.0209 | 3.3291 | 2.4989 | 4.9022 | 1.7687 | 4.8760 | | 1.7685 | 5.7097 | 5.9776 | H16 | 2.9752 | 3.5586 | 2.1670 | 4.1748 | 1.0949 | 5.1508 | 3.0209 | 3.3291 | 3.7745 | 4.2353 | 2.4989 | 4.9022 | 1.7687 | 4.8760 | 1.7685 | | 5.9776 | 5.7097 | H17 | 3.5150 | 2.9224 | 3.8369 | 2.1675 | 5.2996 | 1.0946 | 4.3260 | 3.8075 | 3.6863 | 2.7635 | 3.8480 | 2.4980 | 5.6371 | 1.7675 | 5.7097 | 5.9776 | | 1.7699 | H18 | 2.9224 | 3.5150 | 3.8369 | 2.1675 | 5.2996 | 1.0946 | 3.6863 | 2.7635 | 4.3260 | 3.8075 | 3.8480 | 2.4980 | 5.6371 | 1.7675 | 5.9776 | 5.7097 | 1.7699 | |
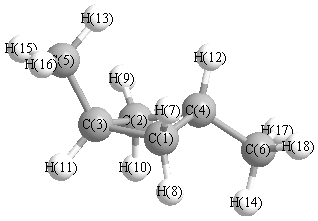 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C3 |
C2 |
88.391 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
C5 |
118.639 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
110.034 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
C2 |
88.222 |
| C1 |
C4 |
C6 |
114.129 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
H12 |
114.833 |
| C2 |
C3 |
C5 |
118.639 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
110.034 |
| C2 |
C4 |
C6 |
114.129 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H12 |
114.833 |
| C3 |
C1 |
C4 |
89.279 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.596 |
| C3 |
C1 |
H8 |
117.441 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
C4 |
89.279 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H9 |
111.596 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H10 |
117.441 |
| C3 |
C5 |
H13 |
110.883 |
|
C3 |
C5 |
H15 |
111.302 |
| C3 |
C5 |
H16 |
111.302 |
|
C4 |
C1 |
H7 |
112.087 |
| C4 |
C1 |
H8 |
117.048 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H9 |
112.087 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H10 |
117.048 |
|
C4 |
C6 |
H14 |
111.401 |
| C4 |
C6 |
H17 |
111.068 |
|
C4 |
C6 |
H18 |
111.068 |
| C5 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.505 |
|
C6 |
C4 |
H12 |
109.496 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
108.431 |
|
H9 |
C2 |
H10 |
108.431 |
| H13 |
C5 |
H15 |
107.728 |
|
H13 |
C5 |
H16 |
107.728 |
| H14 |
C6 |
H17 |
107.624 |
|
H14 |
C6 |
H18 |
107.624 |
| H15 |
C5 |
H16 |
107.729 |
|
H17 |
C6 |
H18 |
107.886 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBE1PBE/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.406 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.406 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.253 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.266 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.645 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.653 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.220 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.218 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.220 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.218 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.216 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.210 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.212 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.220 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.223 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
H |
0.223 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
H |
0.224 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
H |
0.224 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.015 |
-0.001 |
0.000 |
0.015 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-39.611 |
0.401 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.401 |
-40.841 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-40.476 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.047 |
0.401 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.401 |
-0.797 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.250 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.501 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.230 |
|---|
| xy | 0.401 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.052 |
-0.669 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.669 |
10.871 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.462 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
191.041 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.822 |
