Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B1B95/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -133.225432 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -133.229608 |
| HF Energy | -133.225432 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.025202 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3477 |
3301 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3315 |
3147 |
4.92 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3207 |
3044 |
3.30 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3095 |
2938 |
49.85 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1543 |
1465 |
8.45 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1481 |
1406 |
1.89 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1381 |
1311 |
37.12 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1272 |
1207 |
6.45 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1138 |
1080 |
23.65 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1004 |
953 |
10.40 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
486 |
461 |
11.32 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
1058 |
1004 |
0.20 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
816 |
774 |
12.52 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
682 |
647 |
111.30 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
541 |
514 |
7.27 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 12247.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9493) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11626.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.417 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
1.149 |
-0.371 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-1.188 |
-0.141 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
0.137 |
1.504 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.139 |
0.068 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.053 |
-1.449 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.906 |
0.586 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.3930 | 1.3126 | 1.0952 | 2.1668 | 2.1430 | 1.9132 |
C2 | 1.3930 | | 2.3481 | 2.1300 | 1.0826 | 1.0832 | 3.2011 | N3 | 1.3126 | 2.3481 | | 2.1122 | 3.3331 | 2.5947 | 1.0221 | H4 | 1.0952 | 2.1300 | 2.1122 | | 2.4630 | 3.0919 | 2.2392 | H5 | 2.1668 | 1.0826 | 3.3331 | 2.4630 | | 1.8663 | 4.0773 | H6 | 2.1430 | 1.0832 | 2.5947 | 3.0919 | 1.8663 | | 3.5913 | H7 | 1.9132 | 3.2011 | 1.0221 | 2.2392 | 4.0773 | 3.5913 | |
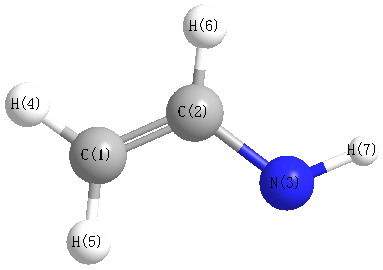 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
H5 |
121.648 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H6 |
119.337 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H7 |
109.438 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
120.396 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.247 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
122.356 |
| H5 |
C2 |
H6 |
119.015 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.035 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.318 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.526 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.173 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.189 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.303 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.039 |
1.610 |
0.000 |
1.916 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-16.468 |
-2.831 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.831 |
-17.401 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.778 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.121 |
-2.831 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.831 |
0.722 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.843 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.687 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.932 |
|---|
| xy | -2.831 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.344 |
-0.441 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.441 |
4.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.742 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
45.018 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.710 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B1B95/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -133.225123 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -133.229282 |
| HF Energy | -133.225123 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.020500 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3423 |
3250 |
11.20 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3295 |
3128 |
9.11 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3189 |
3028 |
3.76 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3162 |
3002 |
24.45 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1527 |
1449 |
4.70 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1476 |
1401 |
4.02 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1403 |
1332 |
12.10 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1262 |
1198 |
33.65 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1167 |
1108 |
32.94 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
997 |
946 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
492 |
467 |
8.80 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
1090 |
1035 |
46.65 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
822 |
780 |
72.14 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
686 |
651 |
8.80 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
497 |
472 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 12244.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9493) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11623.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.446 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
1.126 |
-0.377 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-1.255 |
0.063 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
0.162 |
1.525 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.128 |
0.034 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.023 |
-1.457 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.287 |
-0.962 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.3946 | 1.3117 | 1.0908 | 2.1679 | 2.1614 | 1.9081 |
C2 | 1.3946 | | 2.4208 | 2.1322 | 1.0831 | 1.0856 | 2.4832 | N3 | 1.3117 | 2.4208 | | 2.0354 | 3.3830 | 2.7389 | 1.0260 | H4 | 1.0908 | 2.1322 | 2.0354 | | 2.4680 | 3.1045 | 2.8785 | H5 | 2.1679 | 1.0831 | 3.3830 | 2.4680 | | 1.8560 | 3.5578 | H6 | 2.1614 | 1.0856 | 2.7389 | 3.1045 | 1.8560 | | 2.3631 | H7 | 1.9081 | 2.4832 | 1.0260 | 2.8785 | 3.5578 | 2.3631 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
H5 |
121.563 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H6 |
120.742 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H7 |
108.803 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
126.857 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.641 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
115.502 |
| H5 |
C2 |
H6 |
117.695 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.048 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.346 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.515 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.168 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.179 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.173 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.293 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.143 |
-1.096 |
0.000 |
2.407 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-20.475 |
2.091 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.091 |
-15.982 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.791 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.588 |
2.091 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.091 |
4.151 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.563 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.125 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.493 |
|---|
| xy | 2.091 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.007 |
-0.096 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.096 |
4.197 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.745 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
45.046 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.712 |
