Jump to
S1C2
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/CEP-121G*
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/CEP-121G*
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B1B95/CEP-121G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -44.714760 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -44.728947 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 145.090165 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/CEP-121G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3517 |
3517 |
1.92 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3093 |
3093 |
113.88 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3087 |
3087 |
30.62 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3082 |
3082 |
42.29 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3030 |
3030 |
45.25 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3028 |
3028 |
40.86 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
3026 |
3026 |
29.70 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1500 |
1500 |
3.48 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1482 |
1482 |
10.38 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1481 |
1481 |
7.57 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1394 |
1394 |
6.02 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1377 |
1377 |
1.84 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1338 |
1338 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1273 |
1273 |
9.26 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1180 |
1180 |
2.98 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1051 |
1051 |
1.88 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1010 |
1010 |
7.99 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
923 |
923 |
4.39 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
862 |
862 |
56.80 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
824 |
824 |
0.64 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
769 |
769 |
104.03 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
523 |
523 |
3.16 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
419 |
419 |
1.06 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A' |
371 |
371 |
6.65 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A' |
233 |
233 |
5.50 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
3090 |
3090 |
22.73 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
3081 |
3081 |
98.67 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
3027 |
3027 |
0.41 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
3023 |
3023 |
57.70 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1494 |
1494 |
10.48 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
1480 |
1480 |
6.53 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
1469 |
1469 |
5.45 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
1381 |
1381 |
0.51 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
1367 |
1367 |
2.19 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
1340 |
1340 |
1.24 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
1293 |
1293 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
1222 |
1222 |
18.84 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
1152 |
1152 |
15.43 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
1115 |
1115 |
0.65 |
|
|
|
| 40 |
A" |
1066 |
1066 |
2.78 |
|
|
|
| 41 |
A" |
940 |
940 |
5.13 |
|
|
|
| 42 |
A" |
885 |
885 |
0.51 |
|
|
|
| 43 |
A" |
796 |
796 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 44 |
A" |
436 |
436 |
0.82 |
|
|
|
| 45 |
A" |
226 |
226 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 34876.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 34876.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/CEP-121G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.650 |
1.322 |
0.000 |
| H2 |
0.599 |
2.419 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.718 |
1.058 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-0.009 |
0.746 |
1.262 |
| C5 |
-0.009 |
0.746 |
-1.262 |
| C6 |
-0.009 |
-0.791 |
-1.210 |
| C7 |
-0.009 |
-0.791 |
1.210 |
| N8 |
-0.619 |
-1.347 |
0.000 |
| H9 |
-1.613 |
-1.123 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
0.508 |
1.096 |
2.166 |
| H11 |
0.508 |
1.096 |
-2.166 |
| H12 |
-1.047 |
1.105 |
1.331 |
| H13 |
-1.047 |
1.105 |
-1.331 |
| H14 |
1.030 |
-1.153 |
-1.251 |
| H15 |
1.030 |
-1.153 |
1.251 |
| H16 |
-0.521 |
-1.211 |
-2.085 |
| H17 |
-0.521 |
-1.211 |
2.085 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
H2 |
H3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
C7 |
N8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
H16 |
H17 |
| C1 | | 1.0975 | 1.1005 | 1.5355 | 1.5355 | 2.5225 | 2.5225 | 2.9558 | 3.3317 | 2.1821 | 2.1821 | 2.1680 | 2.1680 | 2.7992 | 2.7992 | 3.4833 | 3.4833 |
H2 | 1.0975 | | 1.7618 | 2.1812 | 2.1812 | 3.4833 | 3.4833 | 3.9578 | 4.1754 | 2.5392 | 2.5392 | 2.4915 | 2.4915 | 3.8087 | 3.8087 | 4.3326 | 4.3326 | H3 | 1.1005 | 1.7618 | | 2.1616 | 2.1616 | 2.8047 | 2.8047 | 3.3541 | 3.9819 | 2.4811 | 2.4811 | 3.0696 | 3.0696 | 2.6322 | 2.6322 | 3.8092 | 3.8092 | C4 | 1.5355 | 2.1812 | 2.1616 | | 2.5236 | 2.9105 | 1.5381 | 2.5193 | 2.7676 | 1.0985 | 3.4838 | 1.1006 | 2.8162 | 3.3164 | 2.1647 | 3.9105 | 2.1838 | C5 | 1.5355 | 2.1812 | 2.1616 | 2.5236 | | 1.5381 | 2.9105 | 2.5193 | 2.7676 | 3.4838 | 1.0985 | 2.8162 | 1.1006 | 2.1647 | 3.3164 | 2.1838 | 3.9105 | C6 | 2.5225 | 3.4833 | 2.8047 | 2.9105 | 1.5381 | | 2.4192 | 1.4646 | 2.0363 | 3.9014 | 2.1777 | 3.3358 | 2.1648 | 1.1007 | 2.6950 | 1.0975 | 3.3604 | C7 | 2.5225 | 3.4833 | 2.8047 | 1.5381 | 2.9105 | 2.4192 | | 1.4646 | 2.0363 | 2.1777 | 3.9014 | 2.1648 | 3.3358 | 2.6950 | 1.1007 | 3.3604 | 1.0975 | N8 | 2.9558 | 3.9578 | 3.3541 | 2.5193 | 2.5193 | 1.4646 | 1.4646 | | 1.0187 | 3.4541 | 3.4541 | 2.8226 | 2.8226 | 2.0788 | 2.0788 | 2.0916 | 2.0916 | H9 | 3.3317 | 4.1754 | 3.9819 | 2.7676 | 2.7676 | 2.0363 | 2.0363 | 1.0187 | | 3.7569 | 3.7569 | 2.6562 | 2.6562 | 2.9239 | 2.9239 | 2.3551 | 2.3551 | H10 | 2.1821 | 2.5392 | 2.4811 | 1.0985 | 3.4838 | 3.9014 | 2.1777 | 3.4541 | 3.7569 | | 4.3314 | 1.7650 | 3.8273 | 4.1234 | 2.4834 | 4.9444 | 2.5272 | H11 | 2.1821 | 2.5392 | 2.4811 | 3.4838 | 1.0985 | 2.1777 | 3.9014 | 3.4541 | 3.7569 | 4.3314 | | 3.8273 | 1.7650 | 2.4834 | 4.1234 | 2.5272 | 4.9444 | H12 | 2.1680 | 2.4915 | 3.0696 | 1.1006 | 2.8162 | 3.3358 | 2.1648 | 2.8226 | 2.6562 | 1.7650 | 3.8273 | | 2.6627 | 4.0097 | 3.0687 | 4.1603 | 2.4909 | H13 | 2.1680 | 2.4915 | 3.0696 | 2.8162 | 1.1006 | 2.1648 | 3.3358 | 2.8226 | 2.6562 | 3.8273 | 1.7650 | 2.6627 | | 3.0687 | 4.0097 | 2.4909 | 4.1603 | H14 | 2.7992 | 3.8087 | 2.6322 | 3.3164 | 2.1647 | 1.1007 | 2.6950 | 2.0788 | 2.9239 | 4.1234 | 2.4834 | 4.0097 | 3.0687 | | 2.5015 | 1.7620 | 3.6790 | H15 | 2.7992 | 3.8087 | 2.6322 | 2.1647 | 3.3164 | 2.6950 | 1.1007 | 2.0788 | 2.9239 | 2.4834 | 4.1234 | 3.0687 | 4.0097 | 2.5015 | | 3.6790 | 1.7620 | H16 | 3.4833 | 4.3326 | 3.8092 | 3.9105 | 2.1838 | 1.0975 | 3.3604 | 2.0916 | 2.3551 | 4.9444 | 2.5272 | 4.1603 | 2.4909 | 1.7620 | 3.6790 | | 4.1698 | H17 | 3.4833 | 4.3326 | 3.8092 | 2.1838 | 3.9105 | 3.3604 | 1.0975 | 2.0916 | 2.3551 | 2.5272 | 4.9444 | 2.4909 | 4.1603 | 3.6790 | 1.7620 | 4.1698 | |
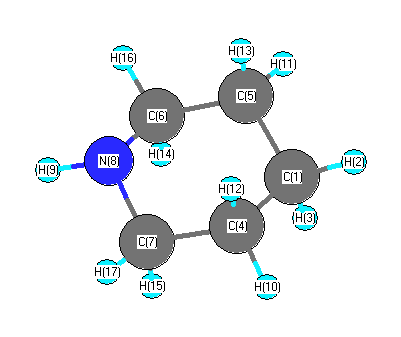 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C4 |
C7 |
110.307 |
|
C1 |
C4 |
H10 |
110.780 |
| C1 |
C4 |
H12 |
109.544 |
|
C1 |
C5 |
C6 |
110.307 |
| C1 |
C5 |
H11 |
110.780 |
|
C1 |
C5 |
H13 |
109.544 |
| H2 |
C1 |
H3 |
106.558 |
|
H2 |
C1 |
C4 |
110.772 |
| H2 |
C1 |
C5 |
110.772 |
|
H3 |
C1 |
C4 |
109.058 |
| H3 |
C1 |
C5 |
109.058 |
|
C4 |
C1 |
C5 |
110.515 |
| C4 |
C7 |
N8 |
114.053 |
|
C4 |
C7 |
H15 |
109.109 |
| C4 |
C7 |
H17 |
110.798 |
|
C5 |
C6 |
N8 |
114.053 |
| C5 |
C6 |
H14 |
109.109 |
|
C5 |
C6 |
H16 |
110.798 |
| C6 |
C5 |
H11 |
110.255 |
|
C6 |
C5 |
H13 |
109.119 |
| C6 |
N8 |
C7 |
111.362 |
|
C6 |
N8 |
H9 |
108.843 |
| C7 |
C4 |
H10 |
110.255 |
|
C7 |
C4 |
H12 |
109.119 |
| C7 |
N8 |
H9 |
108.843 |
|
N8 |
C6 |
H14 |
107.410 |
| N8 |
C6 |
H16 |
108.601 |
|
N8 |
C7 |
H15 |
107.410 |
| N8 |
C7 |
H17 |
108.601 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H12 |
106.755 |
| H11 |
C5 |
H13 |
106.755 |
|
H14 |
C6 |
H16 |
106.551 |
| H15 |
C7 |
H17 |
106.551 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/CEP-121G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.327 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.193 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.163 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.348 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.348 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.351 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
-0.351 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
N |
-0.314 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.286 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.182 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.182 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.155 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.155 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
H |
0.194 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
H |
0.194 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.280 |
1.248 |
0.000 |
1.280 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.728 |
-0.379 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.379 |
-43.776 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-37.846 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.083 |
-0.379 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.379 |
-6.489 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.406 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 4.811 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 7.048 |
|---|
| xy | -0.379 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.852 |
0.219 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.219 |
9.197 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.023 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
0.000 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
0.000 |
