Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3707 |
3551 |
95.09 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3267 |
3129 |
0.79 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3200 |
3065 |
16.16 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3190 |
3055 |
16.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1689 |
1618 |
67.32 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1652 |
1582 |
82.44 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1560 |
1494 |
27.08 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1510 |
1446 |
2.88 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1455 |
1394 |
69.56 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1432 |
1371 |
24.95 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1389 |
1330 |
59.12 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1335 |
1279 |
13.21 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1328 |
1272 |
13.09 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1298 |
1243 |
32.63 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1217 |
1165 |
7.03 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1155 |
1106 |
5.66 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1101 |
1054 |
11.72 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
949 |
909 |
1.56 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
914 |
875 |
12.63 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
815 |
781 |
15.83 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
658 |
630 |
0.55 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
567 |
543 |
4.58 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
448 |
429 |
12.19 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1015 |
972 |
0.42 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
962 |
922 |
5.66 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
901 |
863 |
3.77 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
837 |
802 |
9.31 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
673 |
644 |
6.18 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
631 |
604 |
23.49 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
552 |
529 |
91.64 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
423 |
405 |
2.63 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
248 |
238 |
0.30 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
237 |
227 |
4.27 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21156.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9577) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20262.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
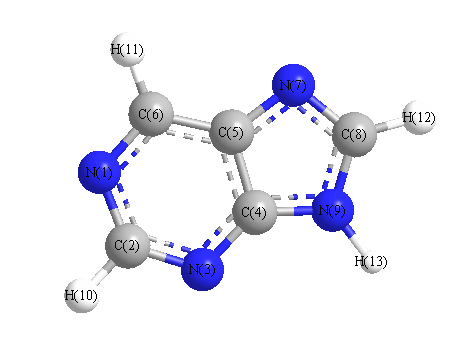
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.296 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.074 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.384 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
0.463 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.199 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.051 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.355 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
0.044 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
N |
-0.426 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.134 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.159 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.295 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.151 |
2.908 |
0.000 |
3.617 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-49.198 |
6.053 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.053 |
-45.965 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-50.565 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.932 |
6.053 |
0.000 |
| y |
6.053 |
3.916 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.984 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.968 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.232 |
|---|
| xy | 6.053 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
14.866 |
1.339 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.339 |
11.525 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.949 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
250.696 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.833 |