Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-31G(2df,p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3241 |
3104 |
4.79 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3233 |
3096 |
9.54 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3223 |
3086 |
8.97 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3216 |
3080 |
4.17 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3205 |
3069 |
0.54 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1697 |
1625 |
64.70 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1669 |
1599 |
0.99 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1632 |
1563 |
130.05 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1506 |
1442 |
4.94 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1495 |
1432 |
20.07 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1390 |
1331 |
12.46 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1325 |
1269 |
5.35 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1202 |
1151 |
35.53 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1181 |
1131 |
0.72 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1141 |
1093 |
105.39 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1095 |
1049 |
6.24 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1044 |
1000 |
5.05 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1015 |
972 |
0.20 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
841 |
805 |
31.14 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
680 |
651 |
7.51 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
610 |
584 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
445 |
426 |
0.72 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
254 |
243 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1024 |
981 |
0.52 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1000 |
957 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
974 |
933 |
3.60 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
882 |
845 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
794 |
760 |
42.06 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
707 |
677 |
18.69 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
479 |
458 |
0.99 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
418 |
401 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
250 |
240 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
116 |
111 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21491.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9577) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20582.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-31G(2df,p)
Charges (e)
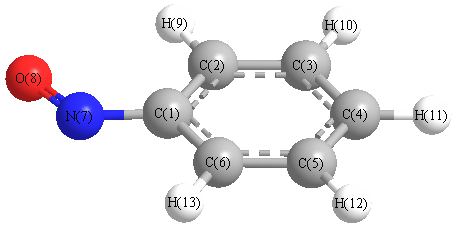
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.307 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.176 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.112 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.111 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.116 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.154 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.047 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
O |
-0.251 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.136 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.083 |
-3.312 |
0.000 |
3.484 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-40.832 |
2.172 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.172 |
-47.080 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-46.284 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.850 |
2.172 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.172 |
-3.523 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.328 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.656 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.249 |
|---|
| xy | 2.172 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
12.218 |
-1.600 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.600 |
14.732 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.623 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
246.033 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.685 |