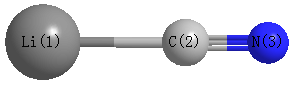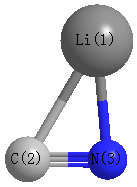Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B1B95/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -99.012911 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -99.011956 |
| HF Energy | -99.012911 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 27.300198 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/STO-3G
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.027 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.179 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.022 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 1.8480 | 3.0492 |
C2 | 1.8480 | | 1.2013 | N3 | 3.0492 | 1.2013 | |
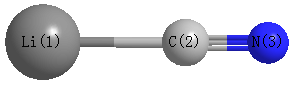 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.241 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.019 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.222 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-6.828 |
6.828 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-13.096 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-13.096 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.046 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.525 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-6.525 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
13.050 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 26.100 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.572 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.572 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.853 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
25.296 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
5.029 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B1B95/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -99.021039 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -99.020521 |
| HF Energy | -99.021039 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 29.483652 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/STO-3G
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
1.252 |
-0.676 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.626 |
-0.403 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.635 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 1.8972 | 1.8129 |
C2 | 1.8972 | | 1.2123 | N3 | 1.8129 | 1.2123 | |
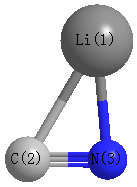 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
67.201 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
74.740 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
38.059 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.227 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.015 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.242 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
4.048 |
-1.860 |
0.000 |
4.455 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.130 |
-4.882 |
0.000 |
| y |
-4.882 |
-14.431 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-13.647 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.909 |
-4.882 |
0.000 |
| y |
-4.882 |
-4.042 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.866 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.733 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 7.301 |
|---|
| xy | -4.882 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.630 |
-0.372 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.372 |
2.065 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.652 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
19.551 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.422 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B1B95/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -99.013456 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -99.012262 |
| HF Energy | -99.013456 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 28.124089 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/STO-3G
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Li1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.821 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.077 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.143 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| Li1 | | 2.8986 | 1.6786 |
C2 | 2.8986 | | 1.2200 | N3 | 1.6786 | 1.2200 | |
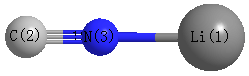 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Li1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Li1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
Li1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Li |
0.316 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.005 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.311 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.125 |
6.125 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-12.931 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-12.931 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.586 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.673 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.673 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.345 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 18.690 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.402 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.402 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.317 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
23.188 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
4.815 |