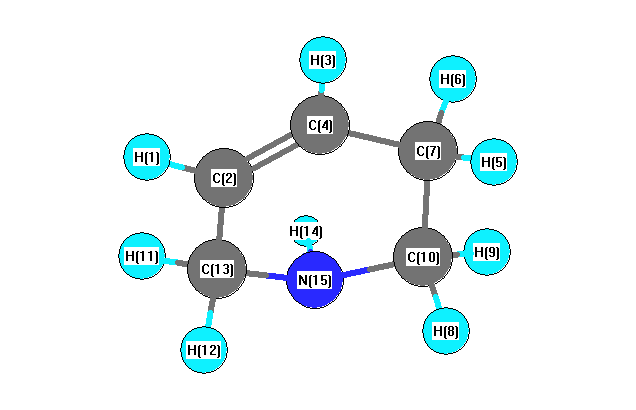
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3506 |
3370 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3186 |
3062 |
34.10 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3160 |
3038 |
9.04 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3103 |
2983 |
38.67 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3076 |
2957 |
25.45 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3067 |
2948 |
48.18 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3044 |
2926 |
27.70 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3019 |
2901 |
35.98 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3005 |
2888 |
46.39 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1747 |
1679 |
2.21 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1484 |
1427 |
6.79 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1455 |
1399 |
2.87 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1441 |
1385 |
9.83 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1436 |
1381 |
1.06 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1409 |
1354 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1384 |
1330 |
7.60 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1360 |
1308 |
4.60 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1332 |
1280 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1317 |
1266 |
0.58 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1250 |
1201 |
5.31 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1217 |
1170 |
16.62 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1182 |
1137 |
4.05 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1142 |
1098 |
10.59 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1098 |
1056 |
2.68 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1060 |
1018 |
5.75 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1007 |
968 |
5.04 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
996 |
958 |
0.15 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
970 |
932 |
2.56 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
934 |
898 |
5.82 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
910 |
875 |
16.06 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
865 |
831 |
0.84 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
817 |
785 |
91.94 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
752 |
722 |
24.86 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
648 |
623 |
20.12 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
522 |
502 |
1.01 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
478 |
459 |
0.43 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
395 |
380 |
1.02 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
287 |
276 |
7.26 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
167 |
161 |
1.97 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29613.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9612) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28464.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
H |
-0.013 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.076 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.011 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.050 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.027 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.032 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
-0.015 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.032 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.016 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
C |
0.040 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.029 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.043 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
C |
0.086 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.084 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
N |
-0.225 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.447 |
0.584 |
-0.485 |
0.881 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-35.536 |
-1.757 |
0.192 |
| y |
-1.757 |
-39.625 |
0.837 |
| z |
0.192 |
0.837 |
-36.594 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.574 |
-1.757 |
0.192 |
| y |
-1.757 |
-3.561 |
0.837 |
| z |
0.192 |
0.837 |
0.987 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.974 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.090 |
|---|
| xy | -1.757 |
|---|
| xz | 0.192 |
|---|
| yz | 0.837 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.740 |
-0.154 |
-0.256 |
| y |
-0.154 |
8.589 |
0.043 |
| z |
-0.256 |
0.043 |
6.703 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
146.183 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.091 |