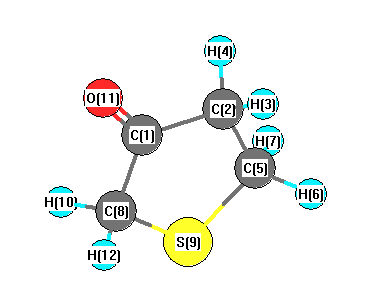
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3155 |
3020 |
5.02 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3150 |
3015 |
0.54 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3134 |
3000 |
8.30 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3082 |
2949 |
24.30 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3069 |
2937 |
14.04 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3067 |
2935 |
3.58 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1849 |
1770 |
235.73 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1490 |
1426 |
2.50 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1440 |
1378 |
1.71 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1438 |
1376 |
17.66 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1306 |
1250 |
13.24 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1293 |
1237 |
10.64 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1229 |
1176 |
12.40 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1219 |
1167 |
21.17 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1166 |
1116 |
10.47 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1154 |
1104 |
35.97 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1095 |
1048 |
2.36 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1010 |
967 |
8.44 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
971 |
929 |
0.51 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
871 |
834 |
6.02 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
834 |
798 |
2.25 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
804 |
770 |
0.54 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
739 |
707 |
5.65 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
693 |
663 |
0.73 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
558 |
534 |
4.38 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
492 |
471 |
4.97 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
449 |
430 |
6.71 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
423 |
405 |
2.64 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
192 |
184 |
1.90 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
64 |
61 |
10.92 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20715.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9571) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19827.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.191 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.236 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.136 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.149 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.226 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.135 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.134 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.206 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
S |
-0.102 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
O |
-0.260 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.140 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.279 |
1.276 |
0.439 |
1.859 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-53.335 |
1.017 |
0.248 |
| y |
1.017 |
-38.337 |
-0.061 |
| z |
0.248 |
-0.061 |
-41.765 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-13.284 |
1.017 |
0.248 |
| y |
1.017 |
9.212 |
-0.061 |
| z |
0.248 |
-0.061 |
4.071 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.142 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -14.997 |
|---|
| xy | 1.017 |
|---|
| xz | 0.248 |
|---|
| yz | -0.061 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.689 |
0.085 |
-0.194 |
| y |
0.085 |
9.956 |
0.047 |
| z |
-0.194 |
0.047 |
7.052 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
182.685 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.516 |