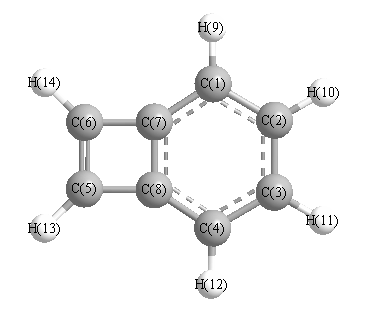
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3263 |
3128 |
15.99 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
3223 |
3090 |
19.30 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
3207 |
3074 |
13.28 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
1736 |
1664 |
3.27 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A1 |
1607 |
1540 |
1.03 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A1 |
1530 |
1467 |
2.87 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A1 |
1457 |
1397 |
10.84 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A1 |
1195 |
1145 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A1 |
1121 |
1074 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A1 |
1072 |
1028 |
0.82 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A1 |
996 |
954 |
5.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A1 |
829 |
795 |
0.53 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A1 |
548 |
525 |
0.15 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A2 |
965 |
925 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A2 |
917 |
879 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A2 |
879 |
843 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A2 |
778 |
745 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A2 |
583 |
558 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A2 |
294 |
282 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B1 |
911 |
874 |
8.28 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B1 |
749 |
718 |
120.81 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B1 |
720 |
690 |
0.75 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B1 |
359 |
344 |
2.74 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B1 |
232 |
222 |
13.76 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B2 |
3232 |
3098 |
4.16 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B2 |
3215 |
3082 |
40.91 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B2 |
3194 |
3062 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B2 |
1685 |
1615 |
0.41 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B2 |
1474 |
1413 |
4.09 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B2 |
1314 |
1259 |
5.34 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B2 |
1261 |
1209 |
12.61 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B2 |
1107 |
1061 |
2.09 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B2 |
1057 |
1013 |
0.73 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B2 |
879 |
843 |
0.64 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B2 |
652 |
625 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B2 |
421 |
403 |
4.31 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24329.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9586) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23322.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.234 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.216 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.216 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.234 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.213 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.213 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
0.047 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
0.047 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.202 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.202 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.209 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.209 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.688 |
0.688 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-50.753 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-40.354 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-39.667 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-10.743 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.856 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.887 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 11.774 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -10.400 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.116 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
13.303 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
16.108 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
218.572 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.784 |