Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3593 |
3444 |
9.95 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3213 |
3080 |
19.69 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3188 |
3056 |
4.21 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3169 |
3038 |
22.58 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1707 |
1637 |
136.59 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1677 |
1607 |
39.59 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1546 |
1482 |
65.54 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1322 |
1268 |
49.07 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1203 |
1153 |
8.54 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1057 |
1013 |
3.51 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1008 |
966 |
0.54 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
969 |
929 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
875 |
838 |
11.49 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
836 |
802 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
760 |
728 |
77.47 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
700 |
671 |
28.76 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
606 |
581 |
304.71 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
530 |
508 |
2.30 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
504 |
483 |
66.87 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
220 |
211 |
5.78 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3693 |
3540 |
7.32 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3194 |
3062 |
48.97 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
3170 |
3039 |
7.08 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1656 |
1587 |
5.40 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1514 |
1451 |
2.06 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1379 |
1322 |
9.36 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1367 |
1311 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1180 |
1131 |
1.81 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1144 |
1097 |
4.14 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1077 |
1033 |
3.98 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
945 |
906 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
818 |
784 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
626 |
600 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
413 |
396 |
0.40 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
374 |
358 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
276 |
265 |
22.24 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25754.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9586) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24688.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
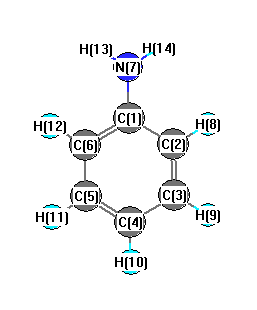
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.280 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.218 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.214 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.211 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.214 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.218 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.851 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.198 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.196 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.194 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.196 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.198 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.333 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.333 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.097 |
1.388 |
0.000 |
1.769 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-46.431 |
-3.442 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.442 |
-33.975 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-36.080 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-11.403 |
-3.442 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.442 |
7.280 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.123 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.246 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -12.456 |
|---|
| xy | -3.442 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.704 |
-0.078 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.078 |
13.920 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.654 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
190.452 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.800 |