Jump to
S1C2
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-311G*
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/6-311G*
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B1B95/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -232.413940 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -232.422187 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 176.835582 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3170 |
3039 |
10.11 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3145 |
3015 |
22.58 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3140 |
3010 |
22.98 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3120 |
2991 |
10.76 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3065 |
2938 |
11.47 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3064 |
2937 |
20.51 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3051 |
2925 |
6.66 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3034 |
2908 |
17.01 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1826 |
1750 |
153.16 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1497 |
1435 |
9.96 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1492 |
1430 |
8.75 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1471 |
1410 |
11.65 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1460 |
1400 |
20.24 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1445 |
1385 |
4.37 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1412 |
1353 |
7.91 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1385 |
1328 |
68.91 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1360 |
1304 |
10.22 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1275 |
1222 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1190 |
1141 |
67.15 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1124 |
1077 |
0.41 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1111 |
1065 |
0.83 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1007 |
966 |
4.85 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
948 |
909 |
4.44 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
938 |
899 |
8.24 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
773 |
741 |
3.38 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
748 |
717 |
2.93 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
594 |
569 |
8.69 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
471 |
452 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
397 |
381 |
4.43 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
253 |
243 |
4.72 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
223 |
213 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
102 |
98 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
51 |
49 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24671.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9586) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 23649.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
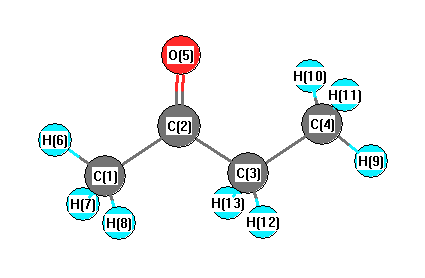
Geometric Data calculated at B1B95/6-311G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.880 |
-0.491 |
0.024 |
| C2 |
0.522 |
0.166 |
-0.015 |
| C3 |
-0.677 |
-0.758 |
-0.042 |
| C4 |
-2.000 |
-0.021 |
0.035 |
| O5 |
0.398 |
1.366 |
-0.017 |
| H6 |
2.655 |
0.253 |
-0.145 |
| H7 |
2.034 |
-0.949 |
1.005 |
| H8 |
1.956 |
-1.290 |
-0.717 |
| H9 |
-2.838 |
-0.718 |
0.007 |
| H10 |
-2.065 |
0.562 |
0.954 |
| H11 |
-2.101 |
0.677 |
-0.795 |
| H12 |
-0.608 |
-1.357 |
-0.958 |
| H13 |
-0.568 |
-1.479 |
0.775 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
| C1 | | 1.5093 | 2.5725 | 3.9086 | 2.3772 | 1.0874 | 1.0934 | 1.0917 | 4.7242 | 4.1878 | 4.2294 | 2.8117 | 2.7454 |
C2 | 1.5093 | | 1.5145 | 2.5296 | 1.2067 | 2.1381 | 2.1374 | 2.1604 | 3.4750 | 2.7907 | 2.7840 | 2.1177 | 2.1264 | C3 | 2.5725 | 1.5145 | | 1.5157 | 2.3809 | 3.4836 | 2.9126 | 2.7701 | 2.1619 | 2.1583 | 2.1572 | 1.0963 | 1.0958 | C4 | 3.9086 | 2.5296 | 1.5157 | | 2.7705 | 4.6661 | 4.2510 | 4.2219 | 1.0905 | 1.0901 | 1.0896 | 2.1692 | 2.1733 | O5 | 2.3772 | 1.2067 | 2.3809 | 2.7705 | | 2.5199 | 3.0133 | 3.1583 | 3.8492 | 2.7659 | 2.7062 | 3.0515 | 3.1076 | H6 | 1.0874 | 2.1381 | 3.4836 | 4.6661 | 2.5199 | | 1.7759 | 1.7877 | 5.5803 | 4.8554 | 4.8185 | 3.7280 | 3.7732 | H7 | 1.0934 | 2.1374 | 2.9126 | 4.2510 | 3.0133 | 1.7759 | | 1.7568 | 4.9786 | 4.3683 | 4.7938 | 3.3166 | 2.6655 | H8 | 1.0917 | 2.1604 | 2.7701 | 4.2219 | 3.1583 | 1.7877 | 1.7568 | | 4.8824 | 4.7314 | 4.5096 | 2.5766 | 2.9385 | H9 | 4.7242 | 3.4750 | 2.1619 | 1.0905 | 3.8492 | 5.5803 | 4.9786 | 4.8824 | | 1.7700 | 1.7704 | 2.5125 | 2.5145 | H10 | 4.1878 | 2.7907 | 2.1583 | 1.0901 | 2.7659 | 4.8554 | 4.3683 | 4.7314 | 1.7700 | | 1.7529 | 3.0750 | 2.5372 | H11 | 4.2294 | 2.7840 | 2.1572 | 1.0896 | 2.7062 | 4.8185 | 4.7938 | 4.5096 | 1.7704 | 1.7529 | | 2.5281 | 3.0768 | H12 | 2.8117 | 2.1177 | 1.0963 | 2.1692 | 3.0515 | 3.7280 | 3.3166 | 2.5766 | 2.5125 | 3.0750 | 2.5281 | | 1.7382 | H13 | 2.7454 | 2.1264 | 1.0958 | 2.1733 | 3.1076 | 3.7732 | 2.6655 | 2.9385 | 2.5145 | 2.5372 | 3.0768 | 1.7382 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
116.588 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O5 |
121.748 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.780 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.376 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H8 |
111.306 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
113.189 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.332 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H13 |
108.034 |
| C3 |
C2 |
O5 |
121.663 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H9 |
111.041 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H10 |
110.779 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H11 |
110.721 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.280 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H13 |
111.644 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.042 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H8 |
110.241 |
| H7 |
C1 |
H8 |
107.030 |
|
H9 |
C4 |
H10 |
108.520 |
| H9 |
C4 |
H11 |
108.596 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H11 |
107.059 |
| H12 |
C3 |
H13 |
104.923 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.355 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.194 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.324 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.329 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.296 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.149 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.145 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.134 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.119 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.133 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.136 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.149 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.256 |
-2.716 |
0.034 |
2.728 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.043 |
-1.033 |
0.134 |
| y |
-1.033 |
-34.917 |
0.021 |
| z |
0.134 |
0.021 |
-30.516 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.673 |
-1.033 |
0.134 |
| y |
-1.033 |
-4.638 |
0.021 |
| z |
0.134 |
0.021 |
1.965 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.929 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.874 |
|---|
| xy | -1.033 |
|---|
| xz | 0.134 |
|---|
| yz | 0.021 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.085 |
-0.204 |
0.027 |
| y |
-0.204 |
7.386 |
-0.001 |
| z |
0.027 |
-0.001 |
5.746 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
135.754 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.651 |
