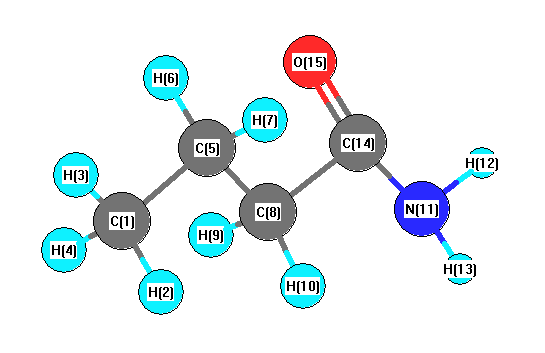
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B1B95/6-31G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3777 |
3603 |
29.19 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3633 |
3465 |
33.89 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3148 |
3002 |
36.52 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3145 |
3000 |
55.03 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3119 |
2975 |
2.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3089 |
2946 |
17.98 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3075 |
2933 |
23.33 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3054 |
2913 |
31.39 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3042 |
2901 |
13.29 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1746 |
1666 |
273.30 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1671 |
1594 |
90.16 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1549 |
1477 |
10.39 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1541 |
1470 |
9.67 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1537 |
1465 |
3.56 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1508 |
1438 |
9.52 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1456 |
1389 |
1.82 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1437 |
1370 |
118.82 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1394 |
1330 |
31.99 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1340 |
1278 |
30.29 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1312 |
1251 |
21.24 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1274 |
1215 |
2.65 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1162 |
1108 |
1.31 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1146 |
1093 |
6.47 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1105 |
1054 |
1.25 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1085 |
1034 |
1.09 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
956 |
912 |
3.18 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
911 |
869 |
3.44 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
869 |
829 |
4.40 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
770 |
735 |
23.54 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
698 |
665 |
111.00 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
623 |
594 |
49.91 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
552 |
526 |
139.04 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
512 |
488 |
53.79 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
430 |
410 |
1.95 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
346 |
330 |
2.88 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
238 |
227 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
184 |
176 |
8.50 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
84 |
80 |
1.73 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
37 |
35 |
3.42 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29277.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9537) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27921.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B1B95/6-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.463 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.157 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.285 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.160 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.191 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.373 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.189 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.761 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.346 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.337 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.525 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.472 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.307 |
-3.861 |
-0.214 |
3.879 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.067 |
-6.560 |
-0.854 |
| y |
-6.560 |
-39.085 |
-0.034 |
| z |
-0.854 |
-0.034 |
-37.671 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.311 |
-6.560 |
-0.854 |
| y |
-6.560 |
-4.216 |
-0.034 |
| z |
-0.854 |
-0.034 |
-2.094 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.189 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 7.018 |
|---|
| xy | -6.560 |
|---|
| xz | -0.854 |
|---|
| yz | -0.034 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.699 |
-0.380 |
-0.184 |
| y |
-0.380 |
7.887 |
0.118 |
| z |
-0.184 |
0.118 |
5.496 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
216.916 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.728 |