Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -581.083806 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -581.002949 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 79.055722 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2290 |
2290 |
0.00 |
376.01 |
0.14 |
0.25 |
| 2 |
Ag |
959 |
959 |
0.00 |
19.26 |
0.11 |
0.20 |
| 3 |
Ag |
594 |
594 |
0.00 |
110.51 |
0.15 |
0.26 |
| 4 |
Au |
552 |
552 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
B1u |
2283 |
2283 |
66.60 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 6 |
B1u |
879 |
879 |
116.29 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 7 |
B2g |
203i |
203i |
0.00 |
36.81 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 8 |
B2u |
2317 |
2317 |
94.89 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 9 |
B2u |
355 |
355 |
20.24 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 10 |
B3g |
2308 |
2308 |
0.00 |
198.95 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
B3g |
603 |
603 |
0.00 |
4.77 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
B3u |
533 |
533 |
0.25 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6734.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6734.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is D2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.067 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.067 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
1.244 |
1.850 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
-1.244 |
1.850 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
1.244 |
-1.850 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-1.244 |
-1.850 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| Si1 | | 2.1339 | 1.4701 | 1.4701 | 3.1711 | 3.1711 |
Si2 | 2.1339 | | 3.1711 | 3.1711 | 1.4701 | 1.4701 | H3 | 1.4701 | 3.1711 | | 2.4887 | 3.6996 | 4.4588 | H4 | 1.4701 | 3.1711 | 2.4887 | | 4.4588 | 3.6996 | H5 | 3.1711 | 1.4701 | 3.6996 | 4.4588 | | 2.4887 | H6 | 3.1711 | 1.4701 | 4.4588 | 3.6996 | 2.4887 | |
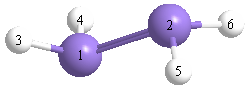 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H5 |
122.174 |
|
Si1 |
Si2 |
H6 |
122.174 |
| Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
122.174 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H4 |
122.174 |
| H3 |
Si1 |
H4 |
115.652 |
|
H5 |
Si2 |
H6 |
115.652 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.038 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.038 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.019 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.019 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.019 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.019 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.023 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-29.469 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-27.545 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.516 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.315 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.201 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.402 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.554 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.157 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
8.260 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
14.691 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
70.293 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.384 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -581.084388 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -581.002768 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 78.529563 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2267 |
2267 |
0.00 |
402.28 |
0.16 |
0.27 |
| 2 |
Ag |
962 |
962 |
0.00 |
20.01 |
0.18 |
0.31 |
| 3 |
Ag |
575 |
575 |
0.00 |
88.20 |
0.15 |
0.26 |
| 4 |
Ag |
273 |
273 |
0.00 |
23.91 |
0.54 |
0.70 |
| 5 |
Au |
2293 |
2293 |
118.35 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 6 |
Au |
536 |
536 |
0.05 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 7 |
Au |
347 |
347 |
18.47 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 8 |
Bg |
2283 |
2283 |
0.00 |
222.64 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
Bg |
612 |
612 |
0.00 |
4.10 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 10 |
Bu |
2262 |
2262 |
98.92 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 11 |
Bu |
917 |
917 |
163.03 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 12 |
Bu |
472 |
472 |
21.73 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6900.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6900.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.078 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.078 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
0.355 |
1.809 |
1.230 |
| H4 |
0.355 |
1.809 |
-1.230 |
| H5 |
-0.355 |
-1.809 |
1.230 |
| H6 |
-0.355 |
-1.809 |
-1.230 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| Si1 | | 2.1567 | 1.4743 | 1.4743 | 3.1586 | 3.1586 |
Si2 | 2.1567 | | 3.1586 | 3.1586 | 1.4743 | 1.4743 | H3 | 1.4743 | 3.1586 | | 2.4604 | 3.6873 | 4.4328 | H4 | 1.4743 | 3.1586 | 2.4604 | | 4.4328 | 3.6873 | H5 | 3.1586 | 1.4743 | 3.6873 | 4.4328 | | 2.4604 | H6 | 3.1586 | 1.4743 | 4.4328 | 3.6873 | 2.4604 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H5 |
119.710 |
|
Si1 |
Si2 |
H6 |
119.710 |
| Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
119.710 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H4 |
119.710 |
| H3 |
Si1 |
H4 |
113.110 |
|
H5 |
Si2 |
H6 |
113.110 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.055 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.055 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.028 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.028 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.028 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.028 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-31.851 |
-0.362 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.362 |
-27.719 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-29.709 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.137 |
-0.362 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.362 |
3.060 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.076 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.153 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.131 |
|---|
| xy | -0.362 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.012 |
-0.544 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.544 |
15.028 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.380 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
70.796 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.414 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -581.047393 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -580.966161 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 73.439994 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
2117 |
2117 |
327.24 |
266.49 |
0.29 |
0.45 |
| 2 |
A1 |
1650 |
1650 |
0.22 |
66.83 |
0.08 |
0.15 |
| 3 |
A1 |
893 |
893 |
29.25 |
61.06 |
0.21 |
0.35 |
| 4 |
A1 |
389 |
389 |
1.03 |
28.46 |
0.19 |
0.33 |
| 5 |
A1 |
374 |
374 |
0.24 |
23.89 |
0.49 |
0.65 |
| 6 |
A2 |
1396 |
1396 |
0.00 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 7 |
A2 |
641 |
641 |
0.00 |
0.17 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 8 |
B1 |
1300 |
1300 |
24.43 |
0.24 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
B1 |
849 |
849 |
17.13 |
3.95 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 10 |
B2 |
2092 |
2092 |
16.76 |
36.46 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
B2 |
1404 |
1404 |
1160.59 |
25.36 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
B2 |
744 |
744 |
94.37 |
0.03 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6923.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 6923.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.310 |
-0.091 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.310 |
-0.091 |
| H3 |
-1.028 |
0.000 |
-0.138 |
| H4 |
1.028 |
0.000 |
-0.138 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
1.350 |
1.416 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-1.350 |
1.416 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| Si1 | | 2.6191 | 1.6655 | 1.6655 | 1.5078 | 3.0572 |
Si2 | 2.6191 | | 1.6655 | 1.6655 | 3.0572 | 1.5078 | H3 | 1.6655 | 1.6655 | | 2.0561 | 2.3012 | 2.3012 | H4 | 1.6655 | 1.6655 | 2.0561 | | 2.3012 | 2.3012 | H5 | 1.5078 | 3.0572 | 2.3012 | 2.3012 | | 2.7006 | H6 | 3.0572 | 1.5078 | 2.3012 | 2.3012 | 2.7006 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H5 |
29.539 |
|
Si1 |
Si2 |
H6 |
91.549 |
| Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
38.163 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H4 |
38.163 |
| H3 |
Si1 |
H4 |
76.232 |
|
H5 |
Si2 |
H6 |
62.010 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.064 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.064 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.056 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.056 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.495 |
0.495 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.435 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-32.167 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.745 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.521 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-1.577 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.944 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.888 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.732 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.775 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
13.837 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.312 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
77.492 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.803 |
