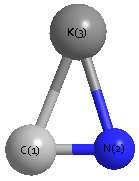Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.460870 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.460241 |
| HF Energy | -692.355839 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 60.494089 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.319 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.292 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.473 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.6115 | 3.7917 |
C2 | 2.6115 | | 1.1802 | N3 | 3.7917 | 1.1802 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.672 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.255 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.417 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
12.127 |
12.127 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.126 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.126 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.341 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.608 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.608 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-7.215 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -14.431 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.220 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.219 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.430 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
101.824 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.091 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.460545 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -692.358417 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.893199 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.221 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.424 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.237 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.6457 | 2.4579 |
C2 | 3.6457 | | 1.1878 | N3 | 2.4579 | 1.1878 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.717 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.140 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.577 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
12.049 |
12.049 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.123 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-23.123 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-32.496 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.687 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.687 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-9.373 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -18.747 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.166 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.166 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.230 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
90.704 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.524 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.468497 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.468418 |
| HF Energy | -692.364096 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 68.223522 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-31G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.046 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.638 |
-1.583 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.547 |
-1.481 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.7053 | 2.5848 |
C2 | 2.7053 | | 1.1888 | N3 | 2.5848 | 1.1888 | |
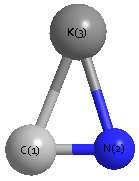 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
71.410 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
82.746 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
25.844 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.637 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.159 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.478 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.433 |
10.003 |
0.000 |
10.012 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.520 |
0.612 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.612 |
-25.948 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.419 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.837 |
0.612 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.612 |
-0.479 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.316 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.631 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.572 |
|---|
| xy | 0.612 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.443 |
-0.050 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.050 |
4.358 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.352 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
71.703 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.468 |