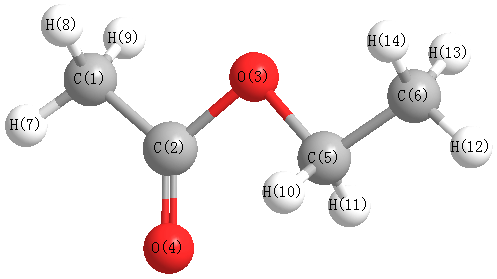
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3215 |
3062 |
6.02 |
60.90 |
0.70 |
0.82 |
| 2 |
A' |
3164 |
3014 |
23.68 |
71.61 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 3 |
A' |
3105 |
2957 |
17.23 |
85.08 |
0.09 |
0.16 |
| 4 |
A' |
3099 |
2952 |
2.56 |
156.02 |
0.01 |
0.01 |
| 5 |
A' |
3085 |
2938 |
18.25 |
137.12 |
0.01 |
0.02 |
| 6 |
A' |
1788 |
1703 |
267.44 |
8.90 |
0.28 |
0.43 |
| 7 |
A' |
1543 |
1470 |
5.17 |
1.66 |
0.64 |
0.78 |
| 8 |
A' |
1525 |
1453 |
3.74 |
12.21 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 9 |
A' |
1499 |
1428 |
15.31 |
8.68 |
0.68 |
0.81 |
| 10 |
A' |
1453 |
1384 |
5.21 |
3.24 |
0.68 |
0.81 |
| 11 |
A' |
1429 |
1361 |
52.66 |
0.63 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 12 |
A' |
1409 |
1342 |
7.85 |
2.02 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 13 |
A' |
1286 |
1224 |
423.05 |
0.86 |
0.53 |
0.69 |
| 14 |
A' |
1151 |
1096 |
9.11 |
7.82 |
0.13 |
0.24 |
| 15 |
A' |
1086 |
1034 |
114.93 |
3.16 |
0.69 |
0.82 |
| 16 |
A' |
1027 |
978 |
6.07 |
1.60 |
0.23 |
0.38 |
| 17 |
A' |
956 |
910 |
9.12 |
2.29 |
0.21 |
0.35 |
| 18 |
A' |
864 |
823 |
12.33 |
9.37 |
0.24 |
0.39 |
| 19 |
A' |
638 |
607 |
6.14 |
8.48 |
0.26 |
0.41 |
| 20 |
A' |
432 |
411 |
0.87 |
0.41 |
0.70 |
0.82 |
| 21 |
A' |
369 |
351 |
8.66 |
3.22 |
0.25 |
0.40 |
| 22 |
A' |
194 |
185 |
5.98 |
0.29 |
0.57 |
0.72 |
| 23 |
A" |
3178 |
3027 |
37.45 |
14.62 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 24 |
A" |
3174 |
3023 |
4.50 |
55.26 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 25 |
A" |
3152 |
3002 |
3.47 |
88.51 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 26 |
A" |
1513 |
1441 |
7.51 |
9.66 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 27 |
A" |
1503 |
1432 |
9.63 |
7.89 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 28 |
A" |
1307 |
1245 |
0.92 |
8.07 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 29 |
A" |
1195 |
1138 |
3.90 |
0.90 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 30 |
A" |
1077 |
1026 |
4.71 |
0.08 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 31 |
A" |
821 |
782 |
0.33 |
0.31 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 32 |
A" |
606 |
577 |
5.71 |
1.04 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 33 |
A" |
267 |
254 |
1.08 |
0.02 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 34 |
A" |
153 |
146 |
5.49 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 35 |
A" |
64 |
61 |
0.30 |
0.41 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 36 |
A" |
31 |
30 |
0.44 |
0.13 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26178.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9524) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24932.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.473 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.460 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.342 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.462 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.075 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.551 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.177 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.174 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.174 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.153 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.153 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.157 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.157 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.364 |
2.056 |
0.000 |
2.088 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.804 |
-1.064 |
-0.005 |
| y |
-1.064 |
-44.021 |
-0.012 |
| z |
-0.005 |
-0.012 |
-36.181 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
9.298 |
-1.064 |
-0.005 |
| y |
-1.064 |
-10.529 |
-0.012 |
| z |
-0.005 |
-0.012 |
1.231 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.462 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 13.218 |
|---|
| xy | -1.064 |
|---|
| xz | -0.005 |
|---|
| yz | -0.012 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.310 |
0.518 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.518 |
8.458 |
0.001 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.001 |
6.372 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
202.719 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.238 |