Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.718039 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.722024 |
| HF Energy | -169.554517 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.583485 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3866 |
3682 |
82.02 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3570 |
3400 |
10.35 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3096 |
2948 |
56.21 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1754 |
1670 |
219.94 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1439 |
1371 |
8.44 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1333 |
1270 |
165.95 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1191 |
1134 |
49.85 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1064 |
1013 |
221.04 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
614 |
585 |
1.66 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1036 |
986 |
2.91 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
831 |
791 |
80.71 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
396 |
377 |
79.41 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10094.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9524) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9614.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.379 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.007 |
-0.532 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.203 |
-0.020 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.335 |
1.421 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.859 |
-0.079 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.832 |
0.780 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3580 | 1.2670 | 1.0947 | 1.9142 | 1.8751 |
O2 | 1.3580 | | 2.2685 | 2.0655 | 0.9647 | 3.1274 | N3 | 1.2670 | 2.2685 | | 2.1071 | 3.0620 | 1.0172 | H4 | 1.0947 | 2.0655 | 2.1071 | | 2.1378 | 2.2597 | H5 | 1.9142 | 0.9647 | 3.0620 | 2.1378 | | 3.7890 | H6 | 1.8751 | 3.1274 | 1.0172 | 2.2597 | 3.7890 | |
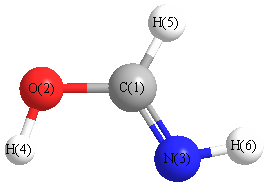 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
109.834 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
109.871 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
119.544 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
114.303 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
126.153 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.156 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.411 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.465 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.118 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.346 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.256 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.093 |
3.541 |
0.000 |
4.113 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.370 |
1.320 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.320 |
-18.546 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.429 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.618 |
1.320 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.320 |
-1.647 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.971 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.942 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.176 |
|---|
| xy | 1.320 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.412 |
-0.098 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.098 |
3.484 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.457 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.823 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.467 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.718039 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.722024 |
| HF Energy | -169.554517 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.583485 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.721639 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.725710 |
| HF Energy | -169.557971 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.449467 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3802 |
3621 |
39.49 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3490 |
3324 |
7.63 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3243 |
3089 |
7.90 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1719 |
1637 |
295.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1423 |
1356 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1336 |
1273 |
38.05 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1117 |
1064 |
262.65 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1080 |
1029 |
53.03 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
584 |
556 |
38.27 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1083 |
1031 |
74.95 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
842 |
802 |
55.47 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
513 |
489 |
86.73 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10116.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9524) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9635.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.442 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.106 |
-0.356 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.230 |
0.126 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.303 |
1.484 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.840 |
-1.288 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.376 |
-0.886 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3636 | 1.2702 | 1.0848 | 1.9233 | 1.9132 |
O2 | 1.3636 | | 2.3847 | 2.0075 | 0.9689 | 2.5380 | N3 | 1.2702 | 2.3847 | | 2.0480 | 2.5067 | 1.0226 | H4 | 1.0848 | 2.0075 | 2.0480 | | 2.8235 | 2.9049 | H5 | 1.9233 | 0.9689 | 2.5067 | 2.8235 | | 2.2526 | H6 | 1.9132 | 2.5380 | 1.0226 | 2.9049 | 2.2526 | |
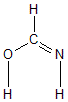 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
109.939 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
112.667 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
129.731 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.633 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
120.636 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.158 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.437 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.431 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.334 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.225 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.955 |
-1.960 |
0.000 |
2.180 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.088 |
-2.229 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.229 |
-13.275 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.349 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.776 |
-2.229 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.229 |
8.443 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.668 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.335 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -10.813 |
|---|
| xy | -2.229 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.986 |
-0.004 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.004 |
3.727 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.423 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.812 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.466 |

