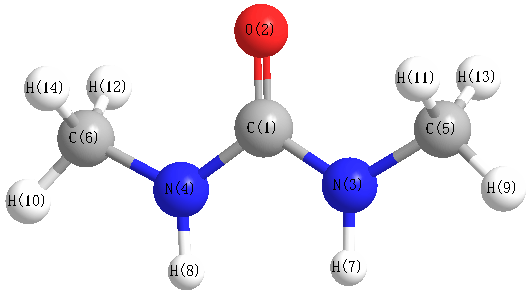
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3650 |
3477 |
25.85 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3203 |
3050 |
10.49 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3155 |
3005 |
9.24 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3071 |
2925 |
6.27 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1761 |
1677 |
279.47 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1550 |
1476 |
15.94 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1518 |
1446 |
0.78 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1496 |
1425 |
8.27 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1473 |
1403 |
8.31 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1213 |
1156 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1188 |
1131 |
1.50 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1156 |
1101 |
7.36 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
929 |
885 |
1.77 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
537 |
511 |
71.63 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
427 |
407 |
53.56 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
224 |
213 |
4.82 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
185 |
177 |
0.20 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
110 |
104 |
0.34 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
3647 |
3473 |
10.32 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3203 |
3050 |
5.30 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3155 |
3005 |
46.54 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
3071 |
2924 |
113.44 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
1579 |
1503 |
363.20 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
1535 |
1462 |
10.05 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1511 |
1439 |
76.50 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1477 |
1406 |
11.57 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1279 |
1218 |
219.00 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1171 |
1115 |
28.79 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1157 |
1102 |
3.77 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1050 |
1000 |
1.71 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
759 |
723 |
18.55 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
730 |
695 |
25.83 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
494 |
470 |
125.51 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
319 |
304 |
42.11 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
126 |
120 |
6.52 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
122 |
116 |
3.87 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26614.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9524) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25347.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.471 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.573 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.449 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.449 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.243 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.243 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.288 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.288 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.134 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.134 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.174 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.174 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.146 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.735 |
3.735 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-38.535 |
-2.083 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.083 |
-30.556 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-38.460 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.027 |
-2.083 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.083 |
7.941 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.914 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -7.828 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -7.979 |
|---|
| xy | -2.083 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.321 |
-0.398 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.398 |
10.164 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.278 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
193.404 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.907 |