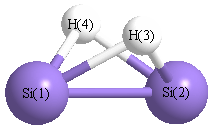Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.774402 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -579.710959 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 67.124615 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σg |
2364 |
2364 |
0.00 |
310.46 |
0.30 |
0.46 |
| 2 |
Σg |
748 |
748 |
0.00 |
75.42 |
0.25 |
0.39 |
| 3 |
Σu |
2361 |
2361 |
0.01 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 4 |
Πg |
604i |
604i |
0.00 |
35.67 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 4 |
Πg |
604i |
604i |
0.00 |
35.67 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
Πu |
413 |
413 |
2.02 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
Πu |
413 |
413 |
2.02 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2545.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2545.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
Point Group is D∞h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.987 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.987 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.446 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.446 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 1.9741 | 1.4585 | 3.4326 |
Si2 | 1.9741 | | 3.4326 | 1.4585 | H3 | 1.4585 | 3.4326 | | 4.8911 | H4 | 3.4326 | 1.4585 | 4.8911 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
180.000 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
-0.049 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
-0.049 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.049 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.049 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-30.313 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-30.313 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-21.290 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.511 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.511 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.023 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 18.046 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.382 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.382 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
14.513 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
56.294 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.503 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
S1C4
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.808380 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -579.741745 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.948408 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
2204 |
2204 |
0.00 |
454.13 |
0.40 |
0.58 |
| 2 |
Ag |
632 |
632 |
0.00 |
35.62 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 3 |
Ag |
572 |
572 |
0.00 |
40.57 |
0.30 |
0.46 |
| 4 |
Au |
415 |
415 |
9.03 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
Bu |
2211 |
2211 |
143.86 |
0.00 |
0.26 |
0.00 |
| 6 |
Bu |
311 |
311 |
33.63 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3172.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3172.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
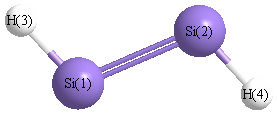
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.053 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.053 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
1.225 |
1.899 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-1.225 |
-1.899 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1064 | 1.4884 | 3.1959 |
Si2 | 2.1064 | | 3.1959 | 1.4884 | H3 | 1.4884 | 3.1959 | | 4.5190 | H4 | 3.1959 | 1.4884 | 4.5190 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
124.609 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
124.609 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.027 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.027 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.027 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.027 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.116 |
-0.246 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.246 |
-23.792 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-31.016 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.712 |
-0.246 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.246 |
6.274 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.562 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -9.124 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.323 |
|---|
| xy | -0.246 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.676 |
0.286 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.286 |
15.211 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.120 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
58.741 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.664 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C4
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.830114 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -579.772429 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 64.746049 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
1624 |
1624 |
8.21 |
93.85 |
0.08 |
0.14 |
| 2 |
A1 |
998 |
998 |
63.69 |
29.99 |
0.45 |
0.62 |
| 3 |
A1 |
527 |
527 |
0.84 |
62.82 |
0.40 |
0.58 |
| 4 |
A2 |
1071 |
1071 |
0.00 |
4.37 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B1 |
1525 |
1525 |
21.30 |
45.31 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
1168 |
1168 |
405.57 |
2.64 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3456.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3456.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.000 |
1.107 |
-0.052 |
| Si2 |
0.000 |
-1.107 |
-0.052 |
| H3 |
0.991 |
0.000 |
0.733 |
| H4 |
-0.991 |
0.000 |
0.733 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.2140 | 1.6807 | 1.6807 |
Si2 | 2.2140 | | 1.6807 | 1.6807 | H3 | 1.6807 | 1.6807 | | 1.9822 | H4 | 1.6807 | 1.6807 | 1.9822 | |
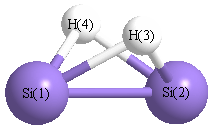 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
48.802 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.802 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.099 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
0.099 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.099 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.099 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.370 |
0.370 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.178 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-32.433 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.919 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.498 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.885 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.387 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.773 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.255 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.362 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
13.483 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.972 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
55.651 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.460 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -579.816922 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -579.755108 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 65.005928 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2202 |
2202 |
101.36 |
328.02 |
0.39 |
0.56 |
| 2 |
A' |
1647 |
1647 |
84.62 |
103.73 |
0.26 |
0.41 |
| 3 |
A' |
1061 |
1061 |
149.15 |
8.49 |
0.59 |
0.74 |
| 4 |
A' |
607 |
607 |
18.84 |
52.54 |
0.35 |
0.52 |
| 5 |
A' |
458 |
458 |
5.01 |
6.36 |
0.23 |
0.37 |
| 6 |
A" |
87 |
87 |
37.51 |
2.95 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3031.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3031.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Si1 |
0.060 |
-1.144 |
0.000 |
| Si2 |
0.060 |
0.975 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
-1.251 |
-0.003 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.438 |
2.376 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Si1 |
Si2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| Si1 | | 2.1193 | 1.7386 | 3.5554 |
Si2 | 2.1193 | | 1.6363 | 1.4871 | H3 | 1.7386 | 1.6363 | | 2.5144 | H4 | 3.5554 | 1.4871 | 2.5144 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Si1 |
Si2 |
H4 |
160.421 |
|
Si2 |
Si1 |
H3 |
48.978 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Si |
0.091 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Si |
-0.024 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
-0.050 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
-0.017 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.034 |
0.858 |
0.000 |
0.859 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.033 |
0.339 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.339 |
-26.584 |
0.006 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.006 |
-31.270 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.894 |
0.339 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.339 |
2.567 |
0.006 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.006 |
-4.461 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -8.922 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.449 |
|---|
| xy | 0.339 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.006 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.013 |
-0.088 |
-0.001 |
| y |
-0.088 |
14.569 |
0.002 |
| z |
-0.001 |
0.002 |
5.553 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
56.818 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.538 |