Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -491.393339 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -491.394085 |
| HF Energy | -491.393339 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 79.710261 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3730 |
3547 |
243.94 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
2106 |
2002 |
679.63 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
896 |
852 |
3.64 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
650 |
618 |
371.94 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
456 |
434 |
79.88 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
487 |
463 |
0.82 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4162.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.951) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3958.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
-0.155 |
1.690 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.496 |
0.000 |
| S3 |
0.036 |
-1.079 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
0.498 |
2.455 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
C2 |
S3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.2040 | 2.7748 | 1.0062 |
C2 | 1.2040 | | 1.5745 | 2.0220 | S3 | 2.7748 | 1.5745 | | 3.5638 | H4 | 1.0062 | 2.0220 | 3.5638 | |
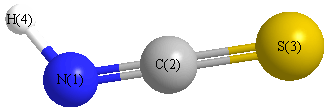 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| N1 |
C2 |
S3 |
173.950 |
|
C2 |
N1 |
H4 |
132.162 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HSEh1PBE/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.602 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.269 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
-0.058 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.391 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.232 |
1.968 |
0.000 |
2.322 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.186 |
3.197 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.197 |
-19.050 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.990 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.166 |
3.197 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.197 |
5.538 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.372 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -6.744 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.136 |
|---|
| xy | 3.197 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.476 |
-0.219 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.219 |
8.714 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.298 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
60.739 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.794 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -491.389354 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -491.389354 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 79.750434 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Σ |
3953 |
3760 |
713.34 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Σ |
2222 |
2114 |
679.38 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Σ |
874 |
831 |
31.62 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Π |
483 |
459 |
4.11 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Π |
483 |
459 |
4.11 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Π |
477i |
454i |
184.82 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Π |
477i |
454i |
184.82 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3530.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.951) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3357.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HSEh1PBE/6-31G*
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| N1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.678 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.498 |
| S3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.088 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.670 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
N1 |
C2 |
S3 |
H4 |
| N1 | | 1.1800 | 2.7657 | 0.9921 |
C2 | 1.1800 | | 1.5857 | 2.1721 | S3 | 2.7657 | 1.5857 | | 3.7578 | H4 | 0.9921 | 2.1721 | 3.7578 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| N1 |
C2 |
S3 |
180.000 |
|
C2 |
N1 |
H4 |
180.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HSEh1PBE/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.594 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.305 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
-0.104 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.393 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.326 |
3.326 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.930 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-24.930 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-15.539 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.695 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.695 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.390 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 18.781 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.292 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.292 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.445 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
60.872 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.802 |
